Soil Conditions
Learn what soil conditions mean in Canadian real estate and how they impact construction, foundations, and property suitability for development.

June 05, 2025
What are Soil Conditions?
Soil conditions refer to the physical and chemical properties of soil on a given property, including composition, stability, moisture retention, and load-bearing capacity.
Why Soil Conditions Matter in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate and construction, soil conditions influence a property's suitability for development and determine foundation requirements, drainage systems, and long-term structural stability.
Soil analysis typically examines:
• Grain size and texture (e.g., clay, sand, loam)
• Bearing capacity and compaction
• Water table level and drainage
• Risk of shifting, erosion, or frost heave
Unfavorable soil conditions may require specialized foundations, soil remediation, or engineering interventions. These conditions are especially relevant for new construction or rural and sloped properties.
Understanding soil conditions helps developers, builders, and buyers anticipate costs, mitigate risk, and ensure safe, code-compliant construction.
Example of Soil Conditions in Action
A buyer with $6,000 monthly income and $2,100 in housing costs has a GDS of 35%. Including $500 in other debts, their TDS is 43%—within lender guidelines.
Key Takeaways
• Assesses soil’s ability to support structures
• Informs foundation and drainage design
• Key for rural, sloped, or undeveloped land
• Helps prevent settling and structural failure
• Often evaluated in geotechnical reports
Related Terms
- Foundation
- Geotechnical Survey
- Drainage System
- Water Table
- Structural Integrity

 205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview
205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview







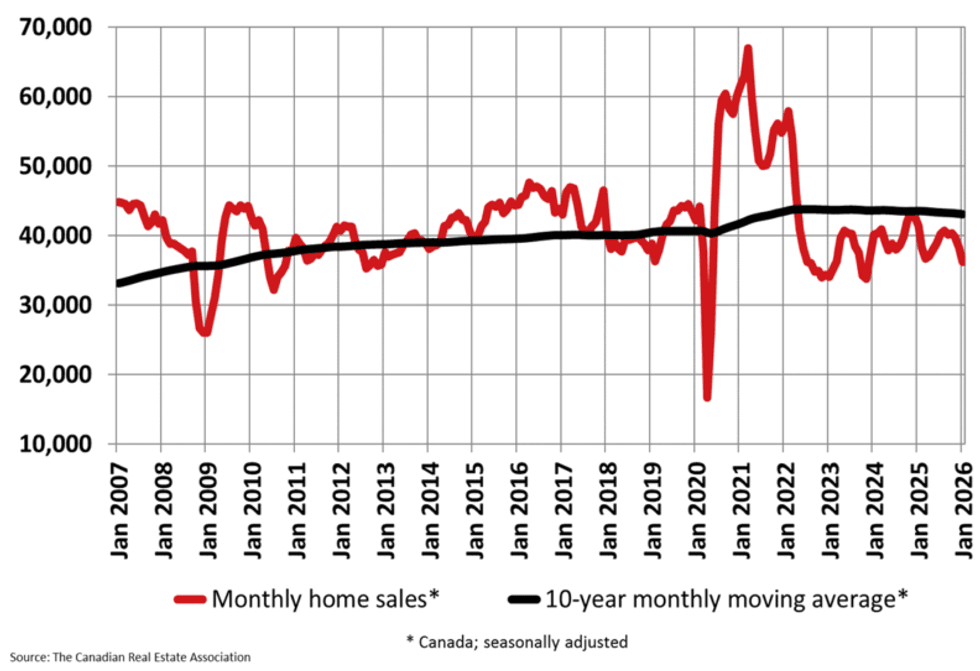 CREA
CREA
 Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)
Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)

 401-415 King Street West. (JLL)
401-415 King Street West. (JLL)
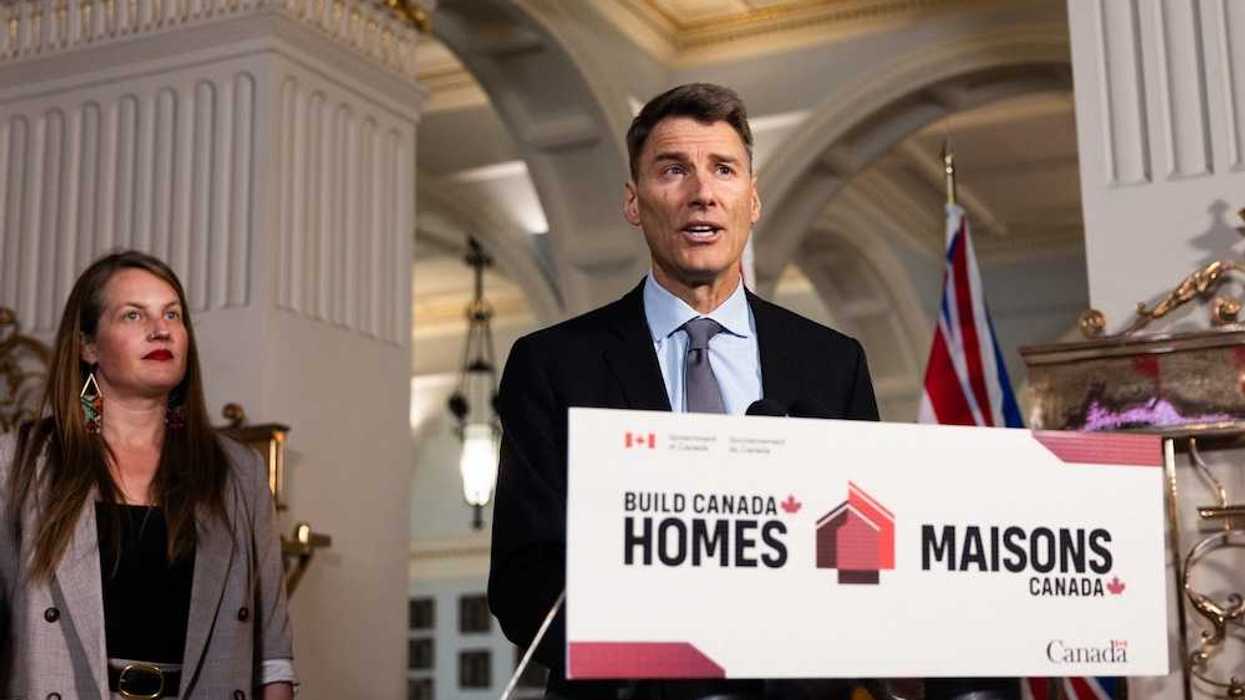
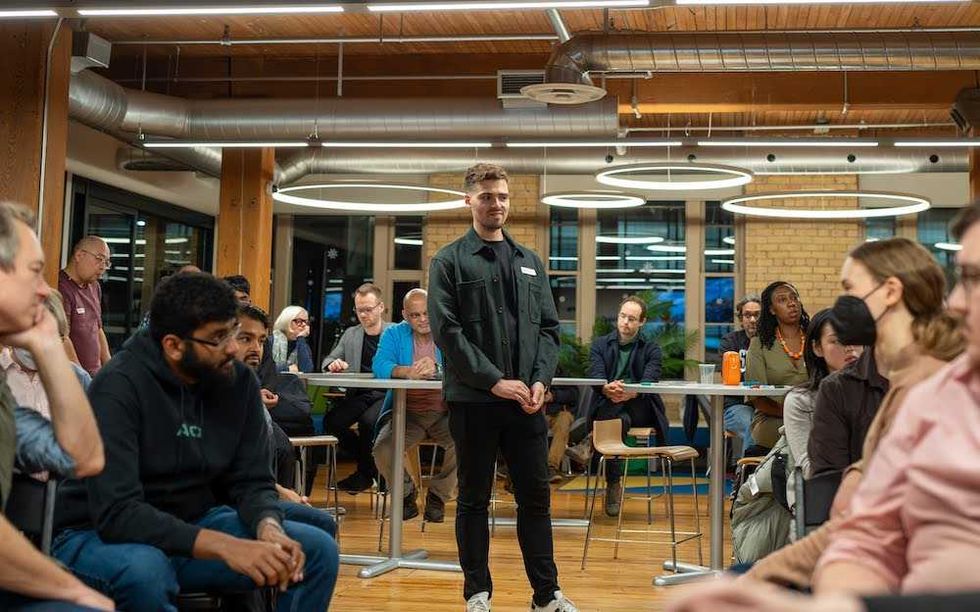 Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.
Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.