Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV)
Learn what the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is in Canadian real estate, how it affects mortgage insurance, and why it matters to both lenders and buyers.

May 22, 2025
What is Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV)?
The Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) is a measure of how much of a property's value is being financed by a mortgage, expressed as a percentage.
Why Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) Matters in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate, LTV helps lenders assess risk when approving a mortgage. A lower LTV means the buyer has more equity, which reduces lender exposure.
LTV formula: LTV = (Mortgage Amount ÷ Appraised Property Value) × 100
LTV benchmarks include:- 80% or lower: typically doesn’t require mortgage insurance
- Above 80%: usually requires CMHC or other mortgage default insurance
LTV also affects interest rates, insurance premiums, and approval conditions. Reducing LTV through a larger down payment can lead to better mortgage terms.
Understanding LTV is essential for evaluating affordability, reducing borrowing costs, and planning long-term equity growth.
Example of Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) in Action
A buyer puts down $100,000 on a $500,000 home. Their mortgage is $400,000, giving them an LTV of 80%.
Key Takeaways
- Shows what portion of the property is financed.
- Lower LTV means less lender risk.
- Impacts insurance and approval.
- Affects rate and terms.
- Key factor in mortgage planning.
Related Terms
- Down Payment
- Mortgage Insurance
- CMHC Insurance
- Home Equity
- Refinance

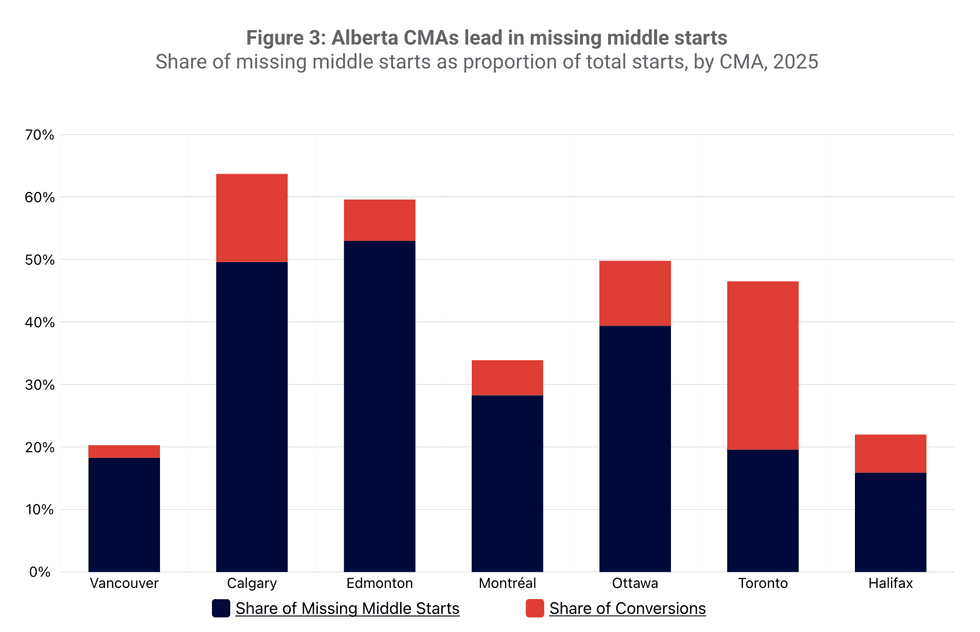 Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC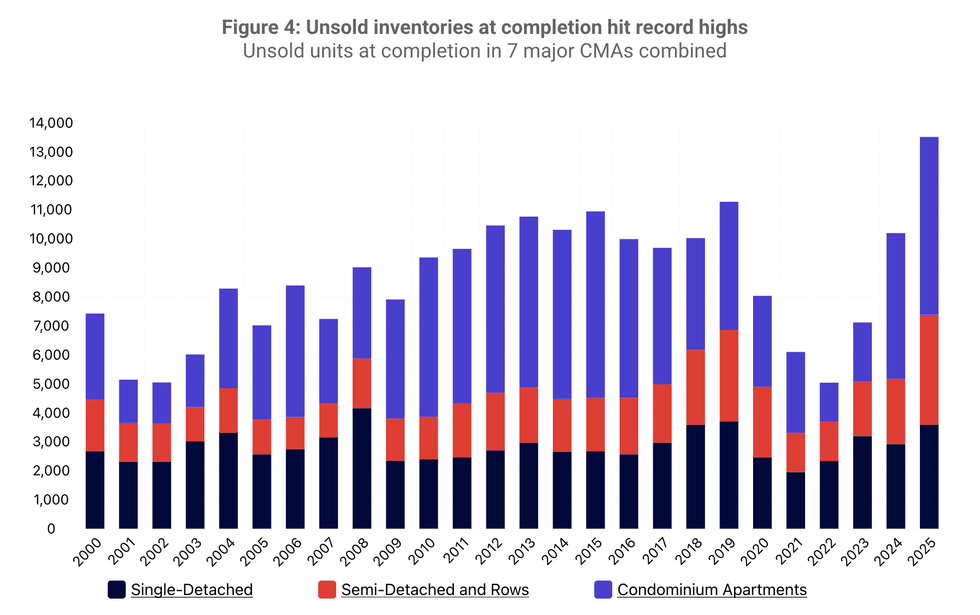 Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC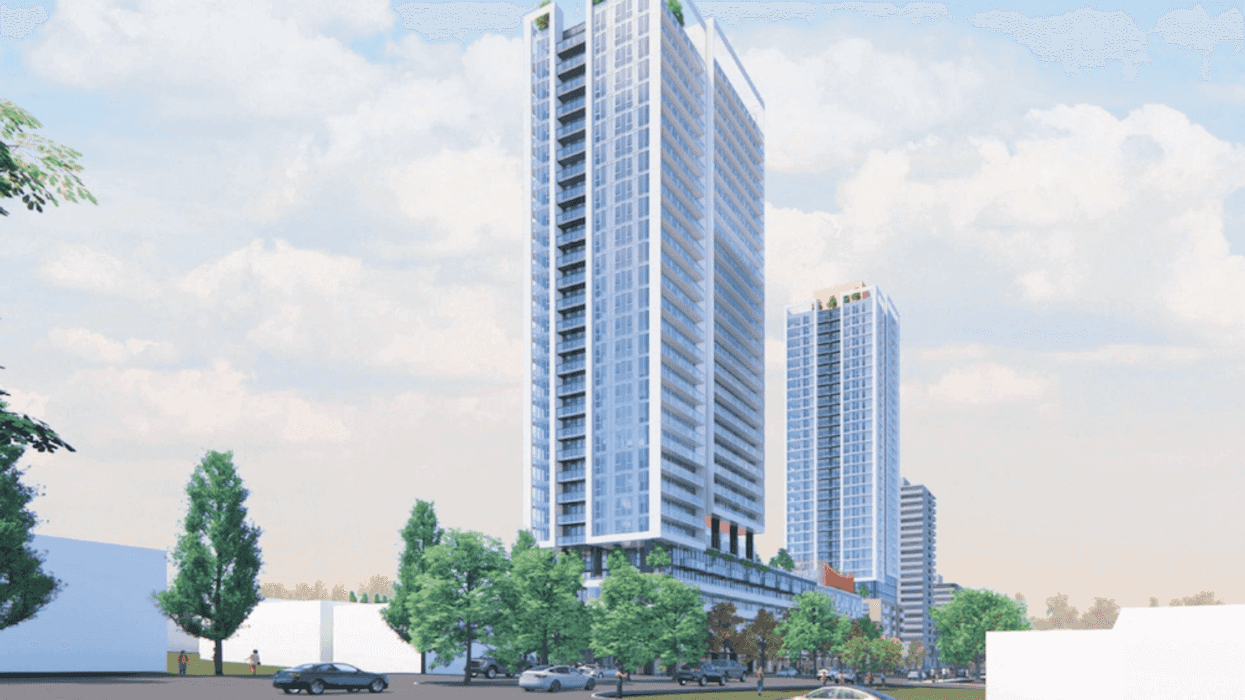
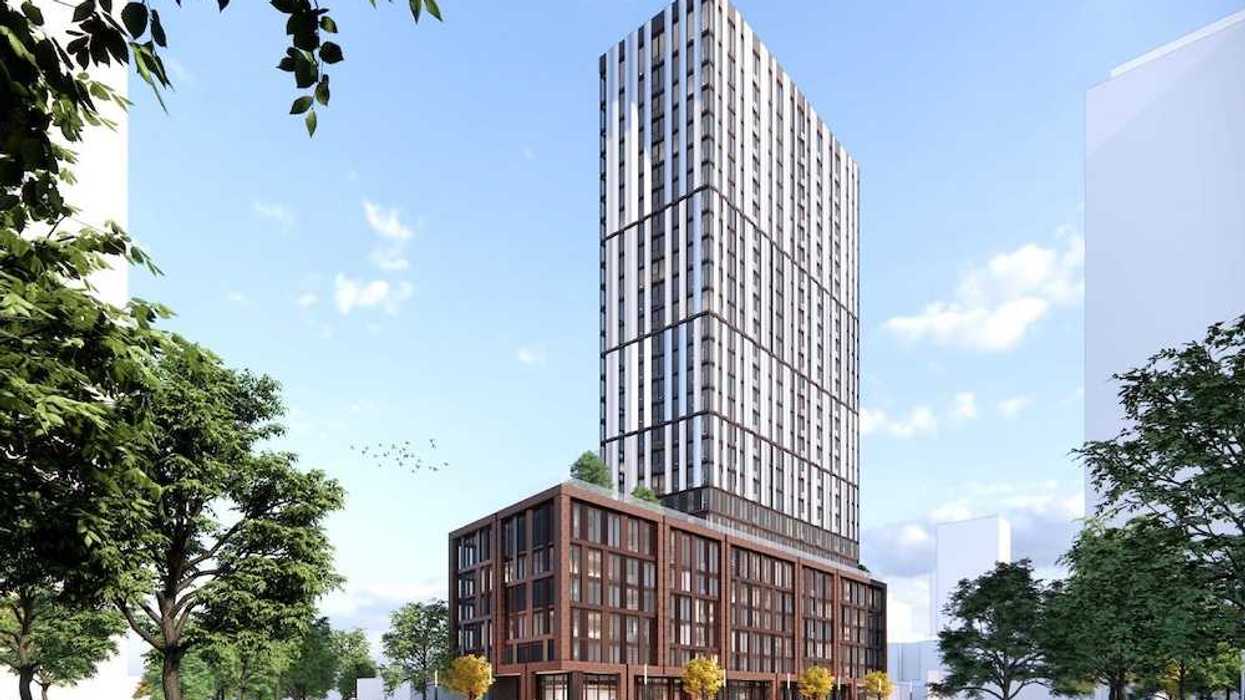
 The Marine Terrace apartments at 605 SE Marine Drive. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
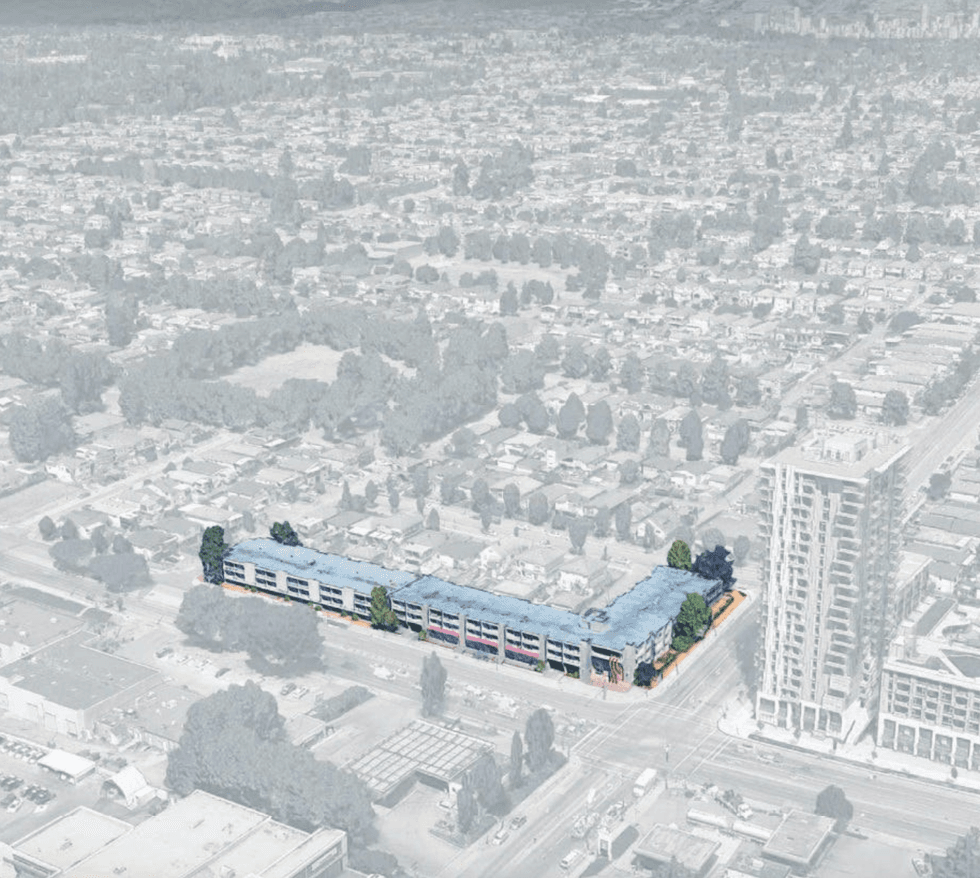
The Marine Terrace apartments at 605 SE Marine Drive. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)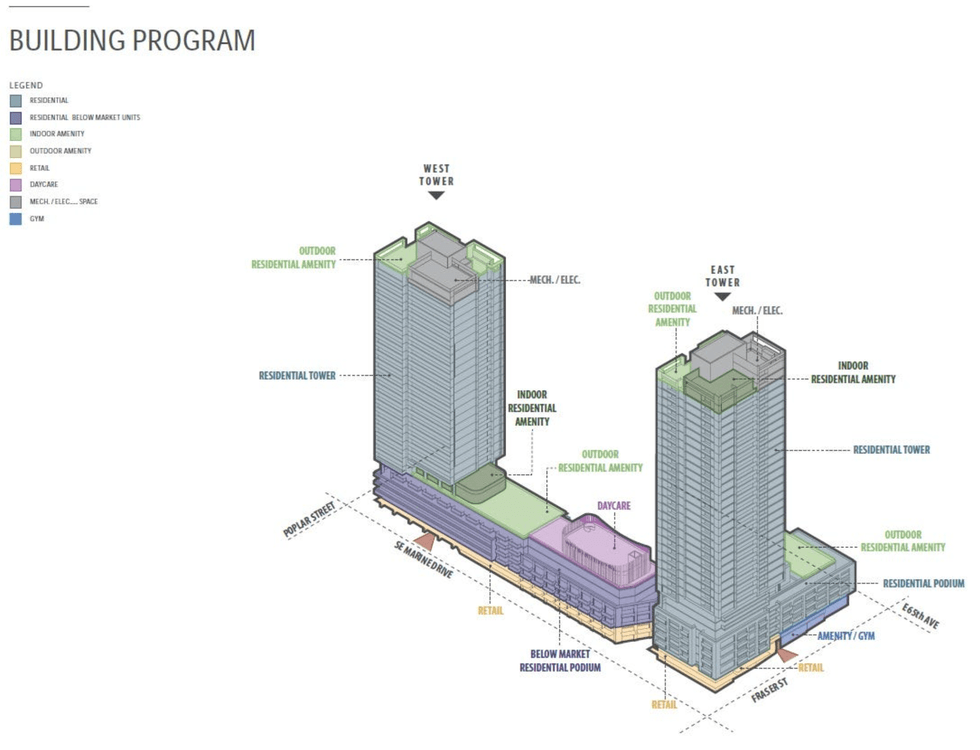 An overview of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal and uses. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
An overview of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal and uses. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)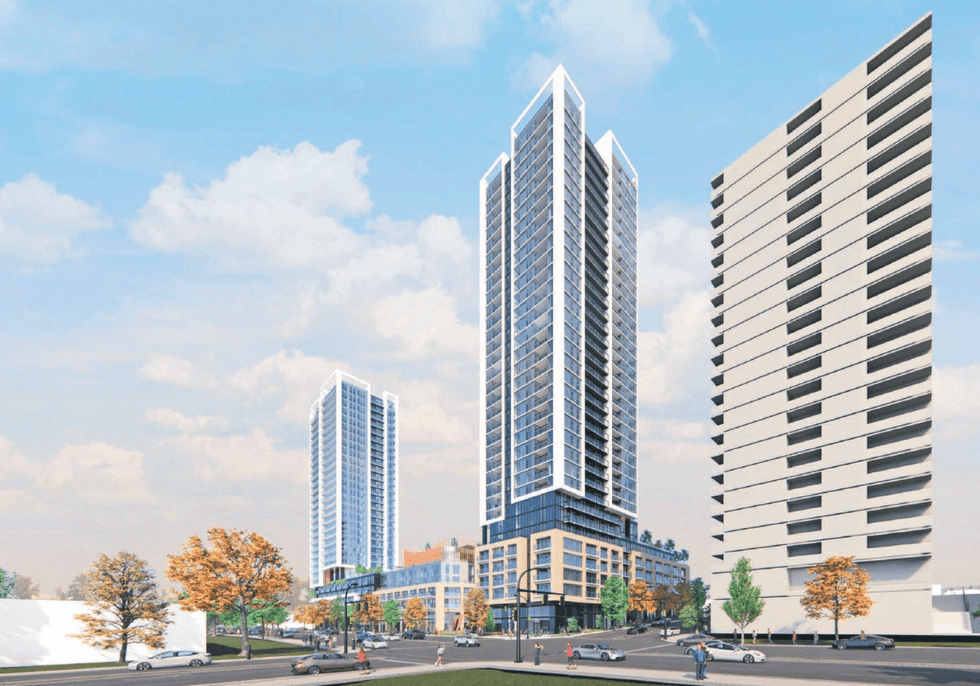 A rendering of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal from the corner of SE Marine Drive and Fraser Street. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
A rendering of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal from the corner of SE Marine Drive and Fraser Street. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)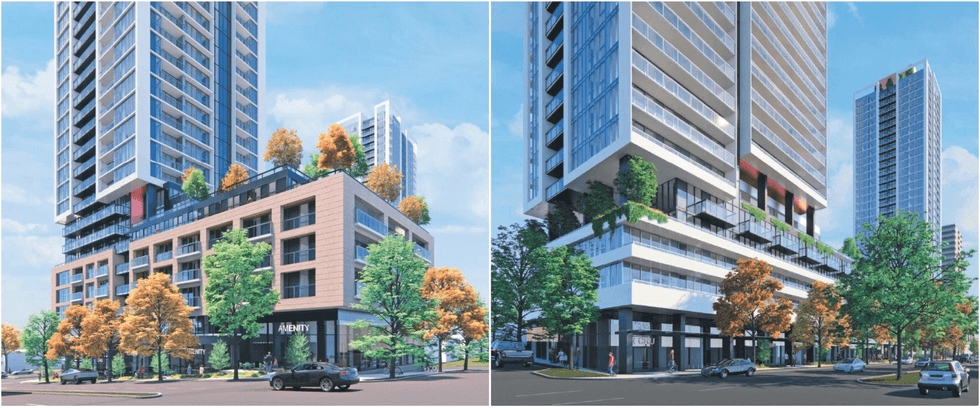
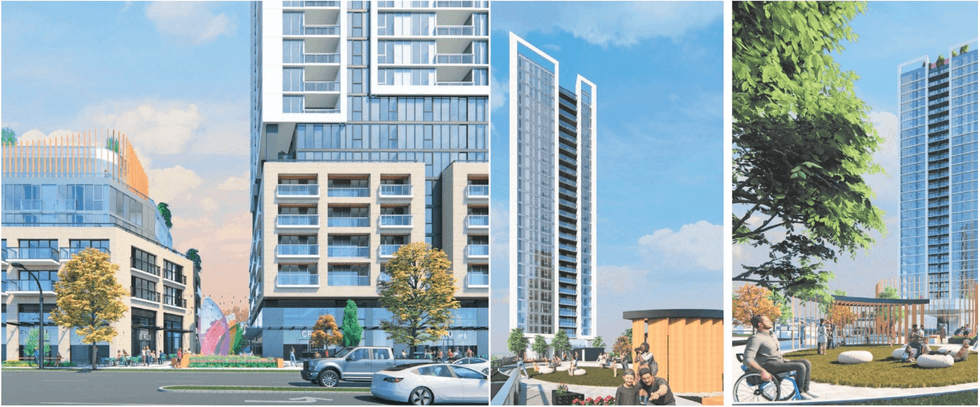 Renderings of the proposal for 605 SE Marine Drive in Vancouver. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
Renderings of the proposal for 605 SE Marine Drive in Vancouver. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)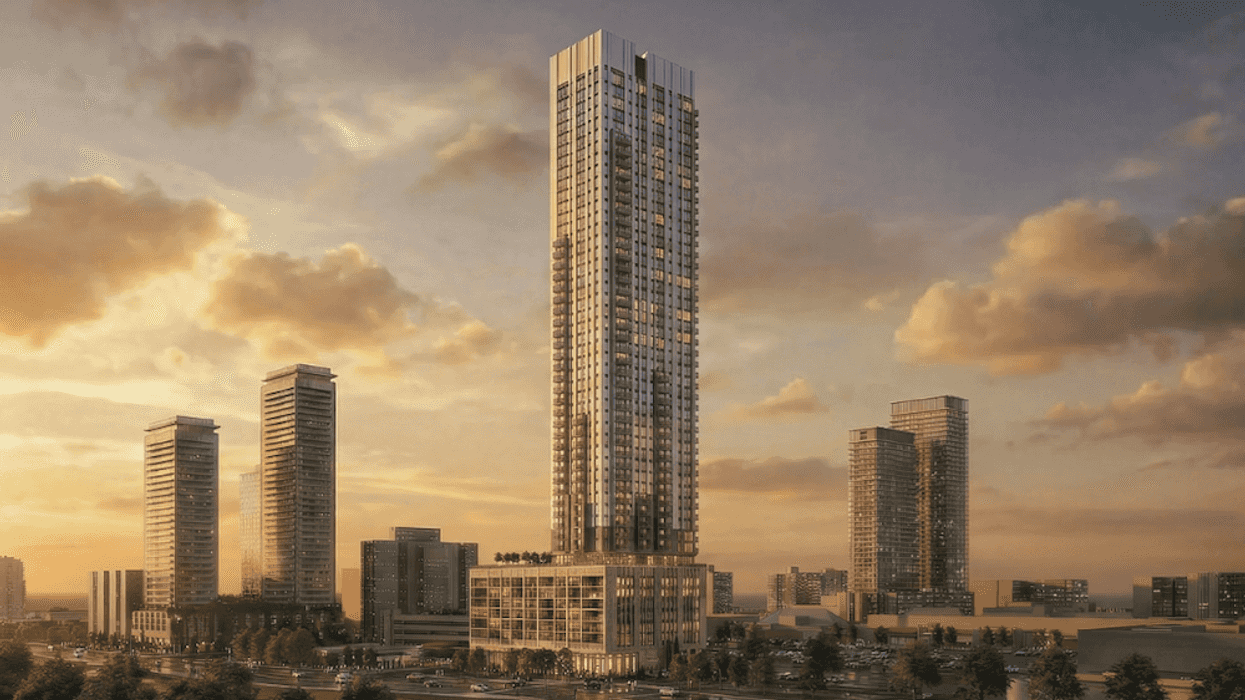
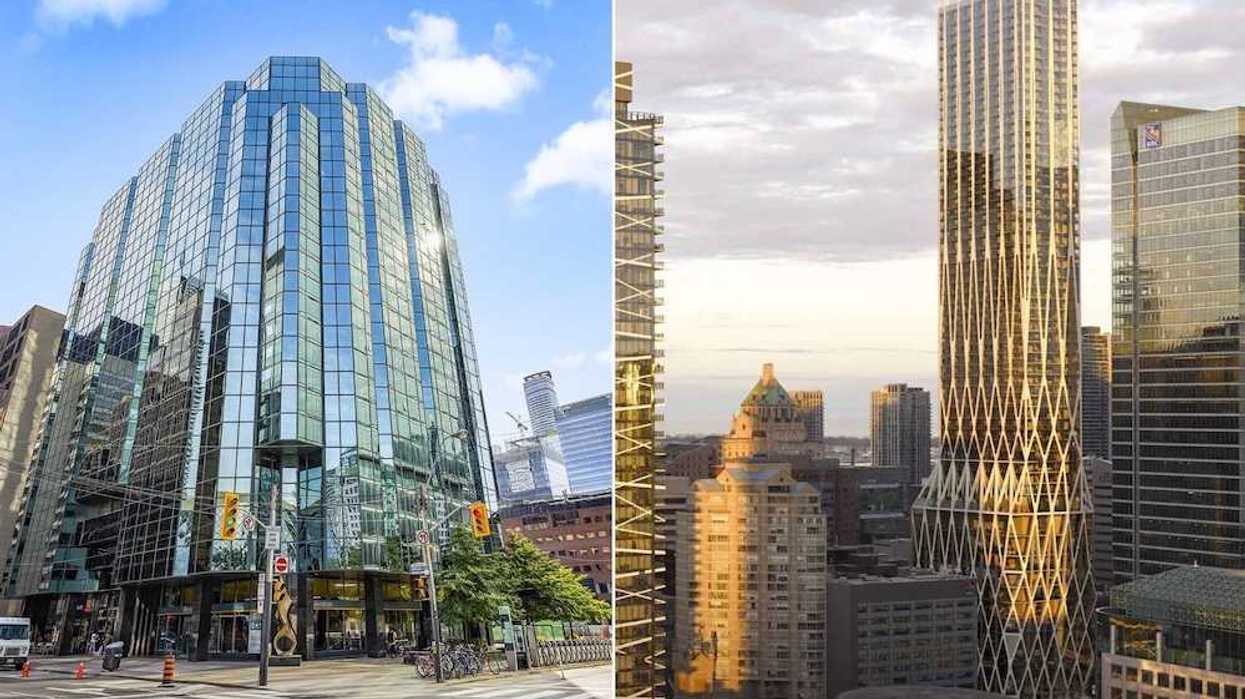
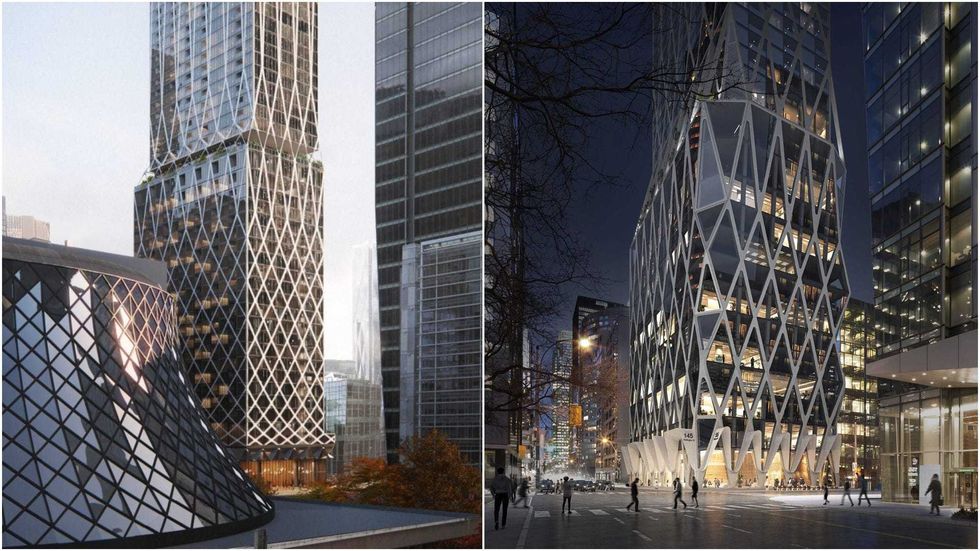









 Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)
Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)