CRA
Learn how the CRA (Canada Revenue Agency) affects real estate in Canada, including capital gains, tax filing, rental income, and the principal residence exemption.

June 13, 2025
What is the CRA?
CRA stands for the Canada Revenue Agency, the federal body responsible for tax administration, compliance, and enforcement in Canada, including taxes related to real estate transactions and property ownership.
Why the CRA Matters in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate, the CRA governs income tax reporting, capital gains, GST/HST on property sales, principal residence exemptions, and rental income obligations.
Key real estate responsibilities under the CRA:
- Reporting rental income and allowable expenses
- Declaring property sales for capital gains tax
- Filing GST/HST on new home sales or flips
- Claiming principal residence exemption (PRE)
- Ensuring compliance with foreign ownership rules
The CRA provides forms, guidance, and audits to ensure compliance. Real estate professionals and homeowners must understand CRA requirements to avoid penalties.
Understanding CRA rules is essential for all property transactions, from investment to ownership transfer and rental income management.
Example of the CRA in Action
The seller reports a gain on their secondary property to the CRA and pays applicable capital gains tax after the sale closes.
Key Takeaways
- Canada's federal tax authority
- Oversees real estate tax obligations
- Manages capital gains and rental income rules
- Handles tax exemptions and credits
- Key to staying compliant as a homeowner or investor
Related Terms
- Capital Gains Tax
- Principal Residence
- Rental Income
- Tax Deduction
- Government Incentive

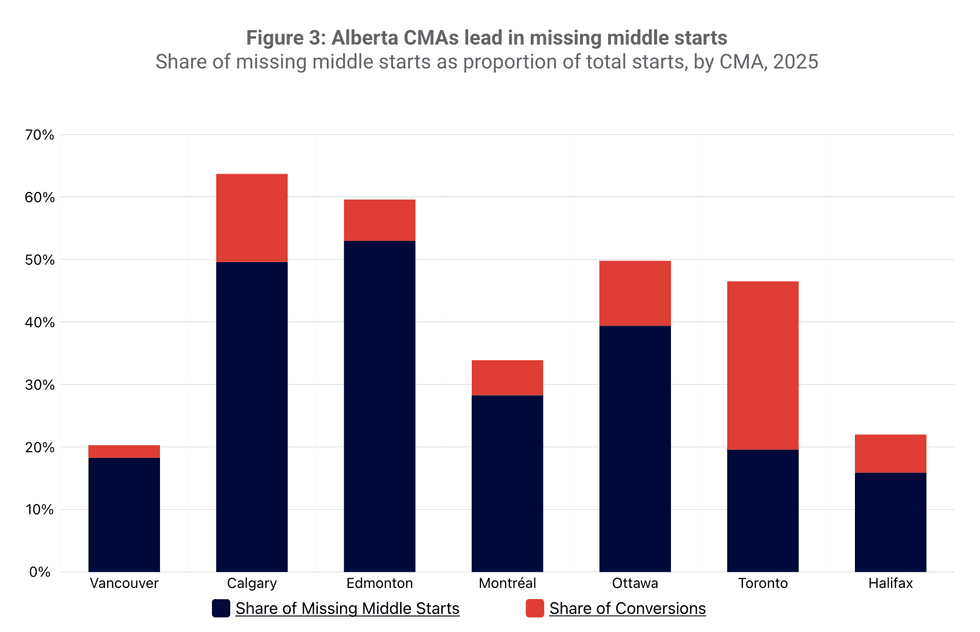 Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC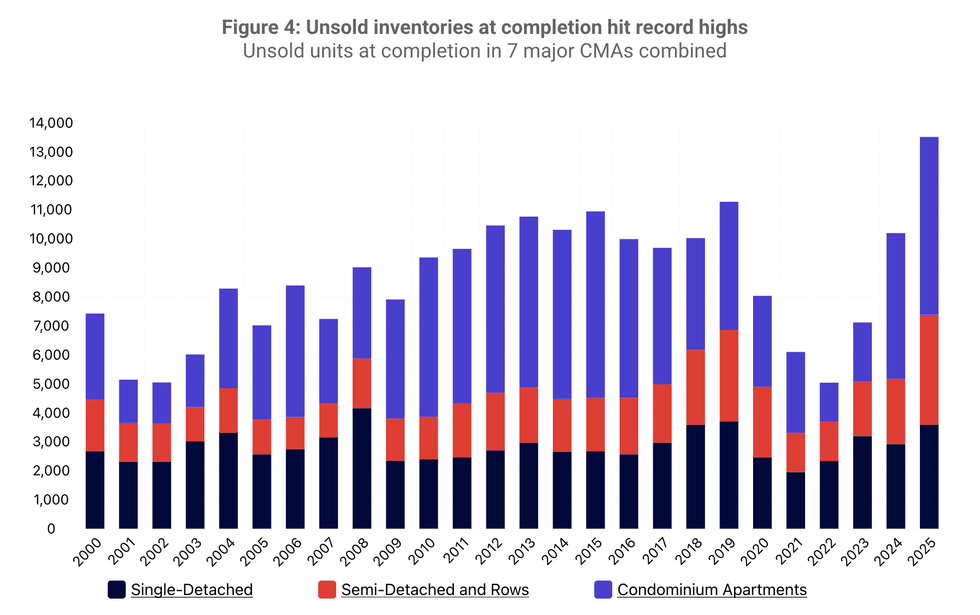 Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC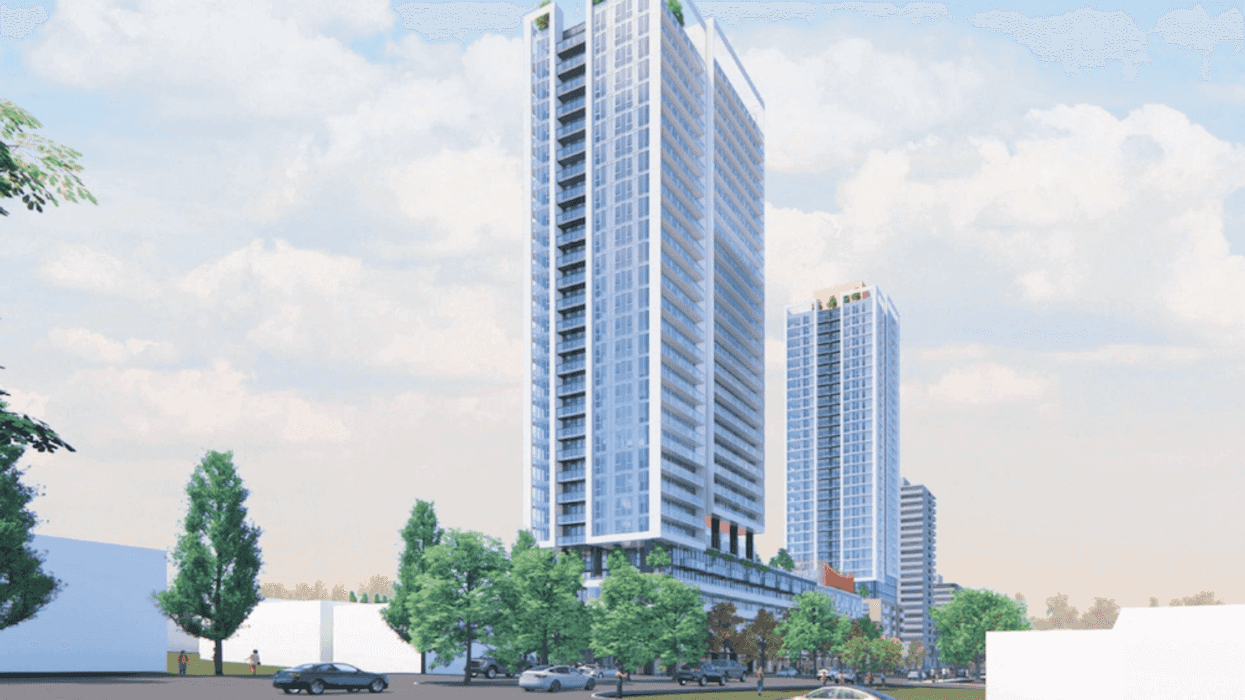
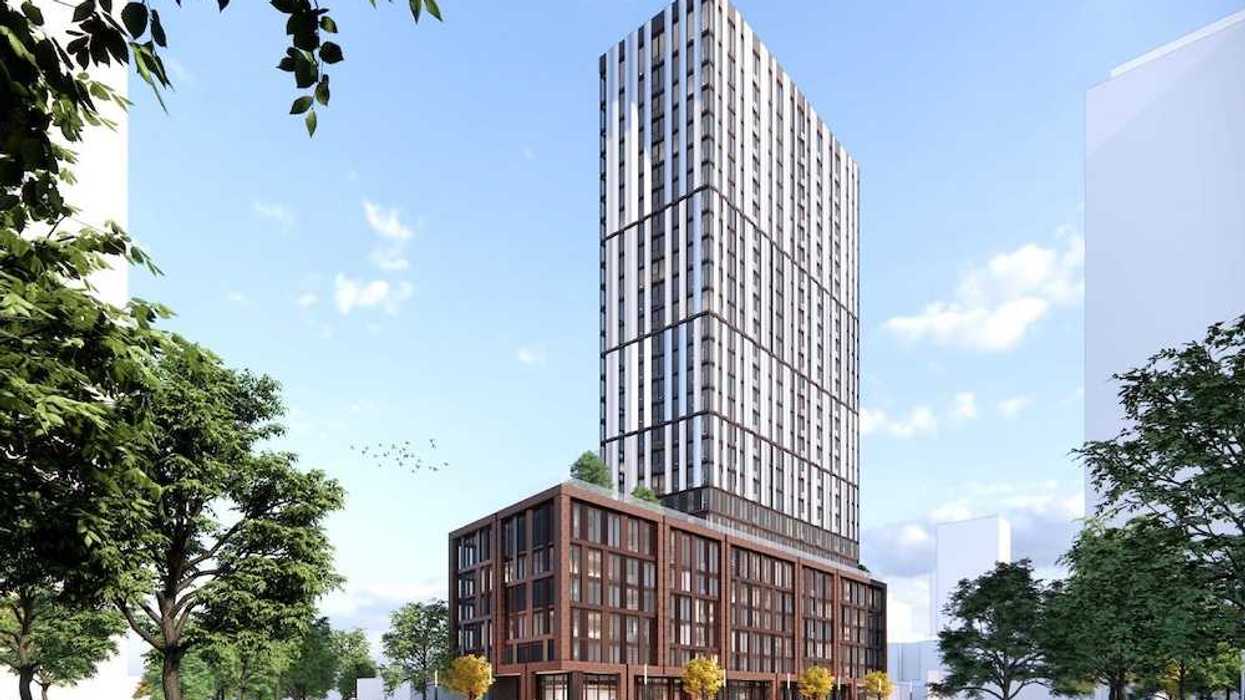
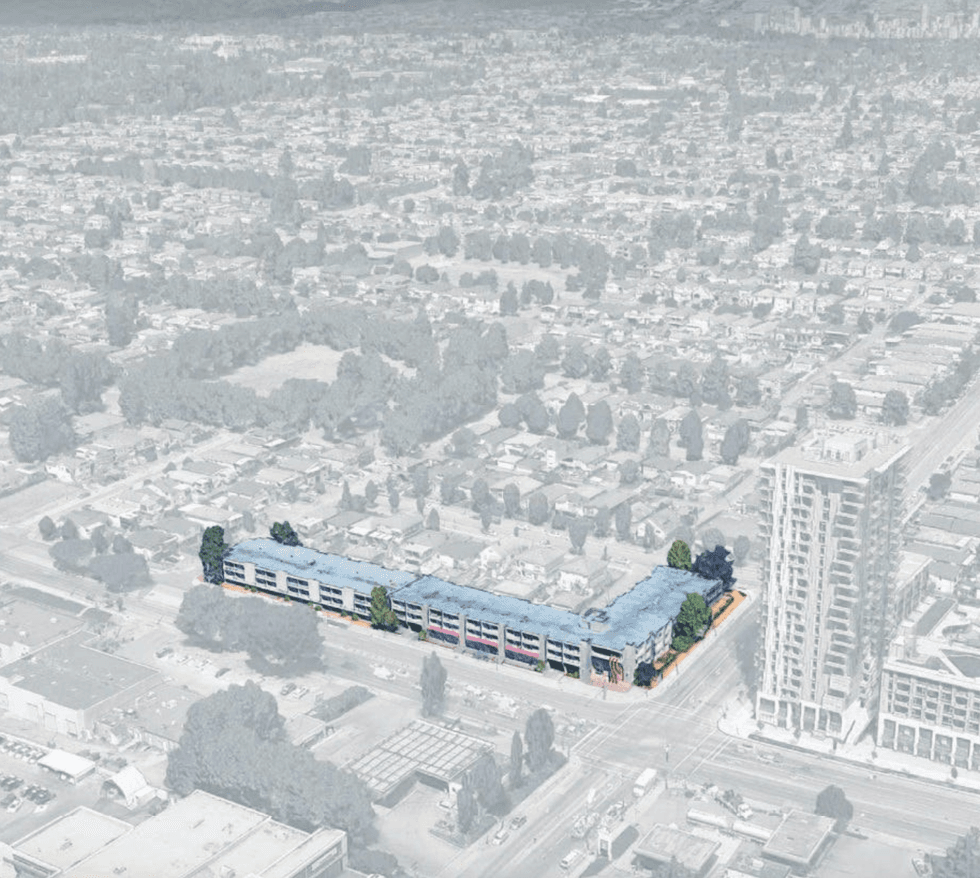 The Marine Terrace apartments at 605 SE Marine Drive. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
The Marine Terrace apartments at 605 SE Marine Drive. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)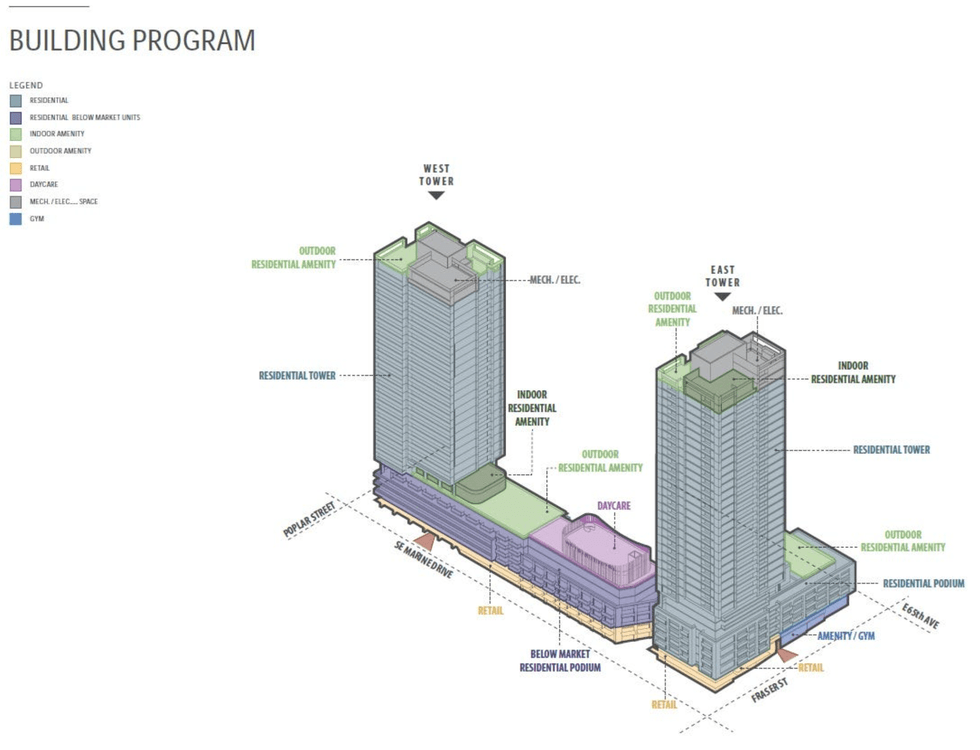 An overview of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal and uses. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
An overview of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal and uses. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)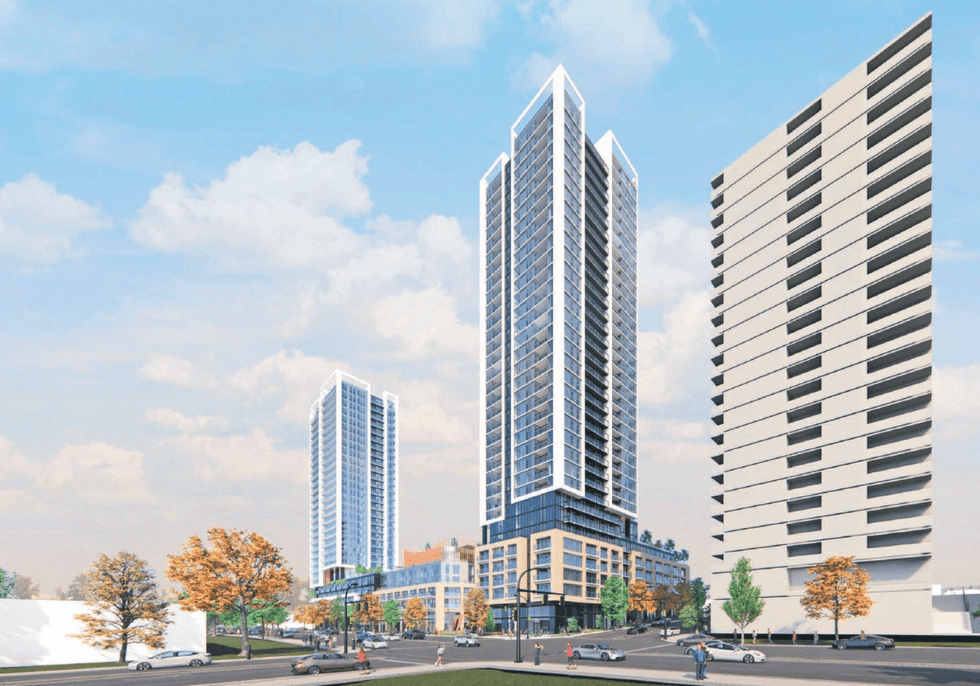 A rendering of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal from the corner of SE Marine Drive and Fraser Street. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
A rendering of the 605 SE Marine Drive proposal from the corner of SE Marine Drive and Fraser Street. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)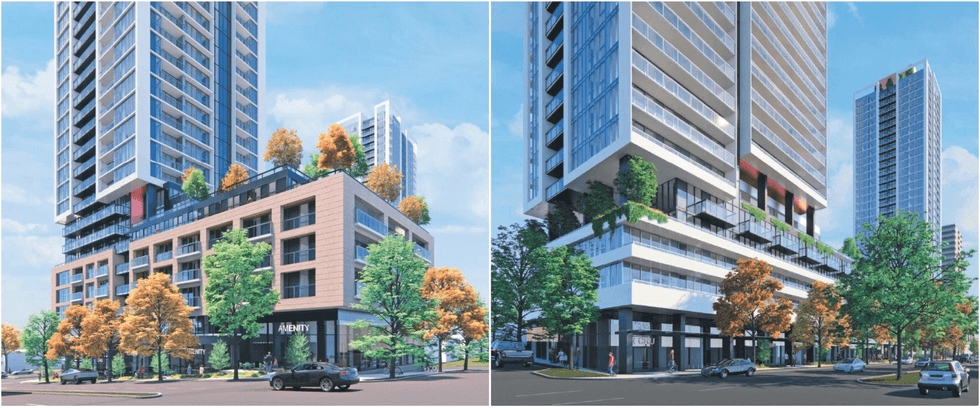
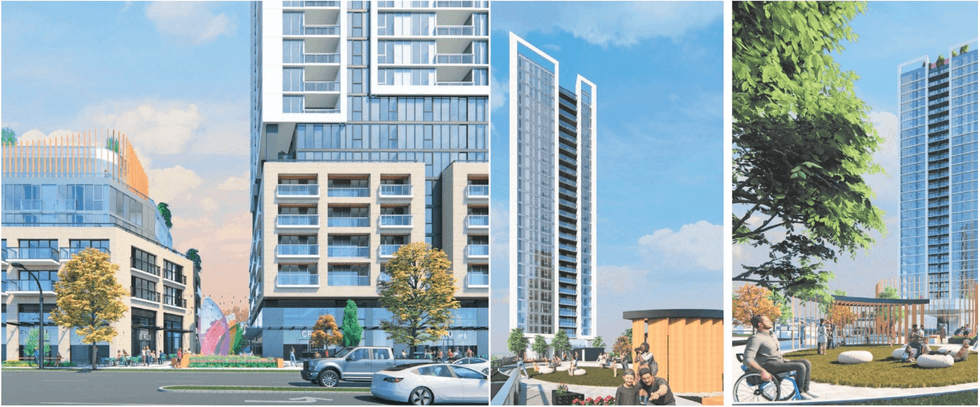 Renderings of the proposal for 605 SE Marine Drive in Vancouver. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)
Renderings of the proposal for 605 SE Marine Drive in Vancouver. (MCMP Architects, Peterson)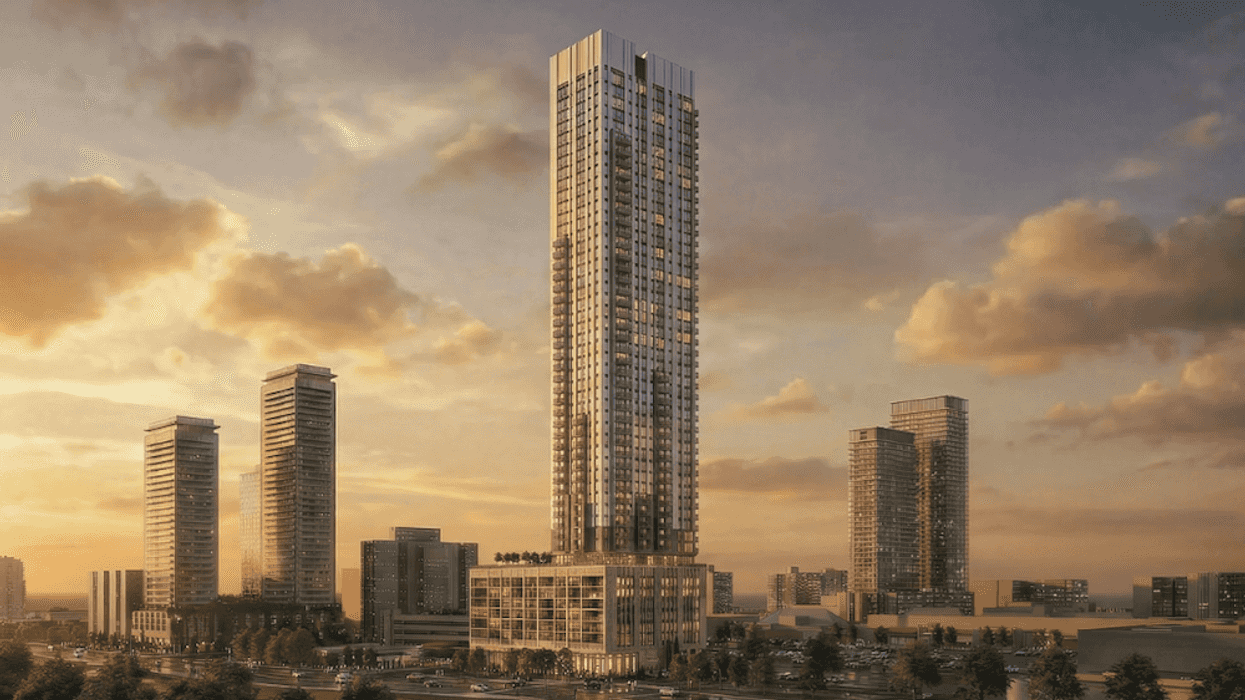
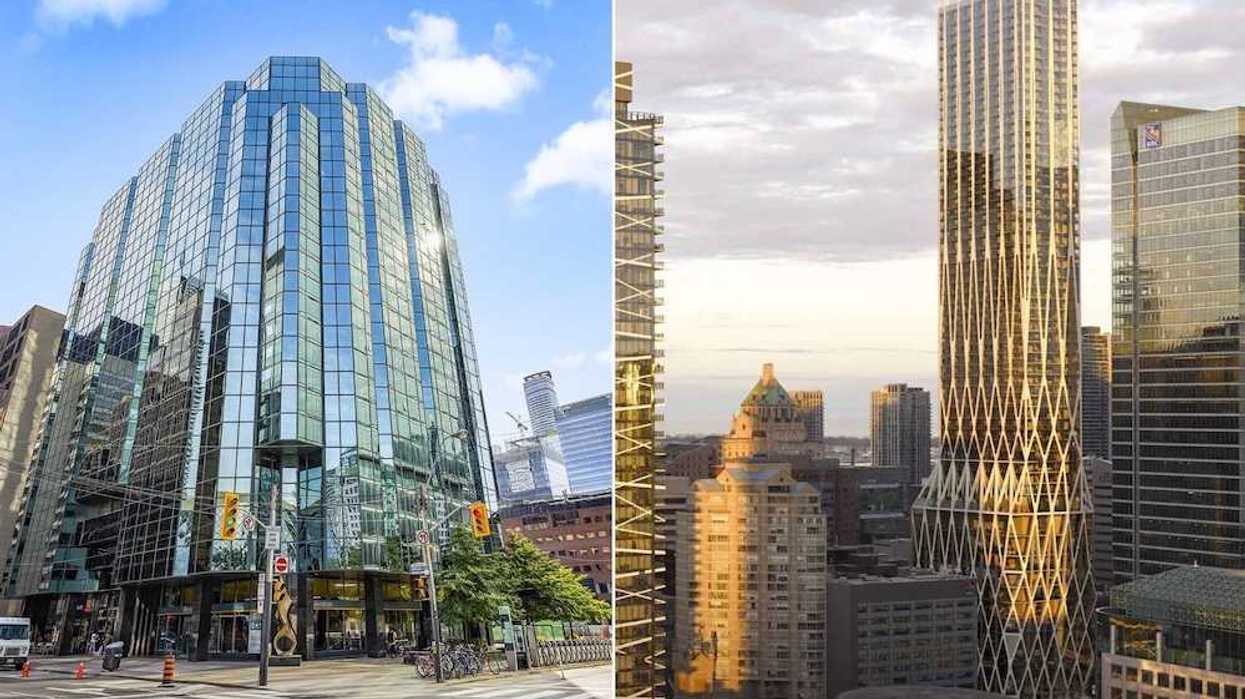
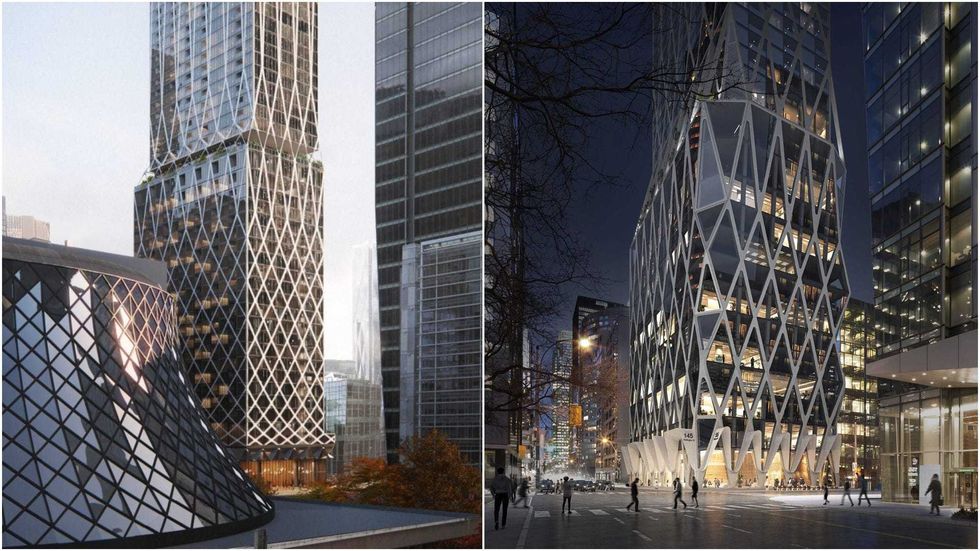









 Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)
Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)