Alternative Financing
Explore what alternative financing means in Canadian real estate, who it's for, and how non-traditional lenders help buyers access the market.

May 22, 2025
What is Alternative Financing?
Alternative financing refers to non-traditional methods of obtaining funding for a real estate purchase, typically used when a borrower does not qualify for a mortgage through a major bank or institutional lender.
Why Alternative Financing Matters in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate, alternative financing plays an important role for buyers with limited credit, unconventional income, or other factors that make them ineligible for traditional mortgages.
Alternative financing sources include:- Private mortgage lenders
- Mortgage investment corporations (MICs)
- Credit unions
- Vendor take-back (VTB) arrangements
- Rent-to-own contracts
Buyers turn to alternative financing when:
- They are self-employed or lack a regular income stream
- Their credit score falls below traditional thresholds
- They are purchasing unconventional or rural properties
Example of Alternative Financing
A self-employed buyer with limited credit history obtains a one-year mortgage from a private lender at 8.5% interest, planning to refinance with a bank after improving their credit score.
Key Takeaways
- Used when traditional mortgage approval is not possible.
- Includes private lenders, MICs, and VTB agreements.
- Offers flexible terms but often higher interest rates.
- Can help bridge financing gaps.
- Requires careful risk and legal review.
Related Terms
- Private Lender
- Mortgage Investment Corporation (MIC)
- Vendor Take-Back Mortgage
- Credit Score
- Non-Conforming Loan

 205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview
205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview







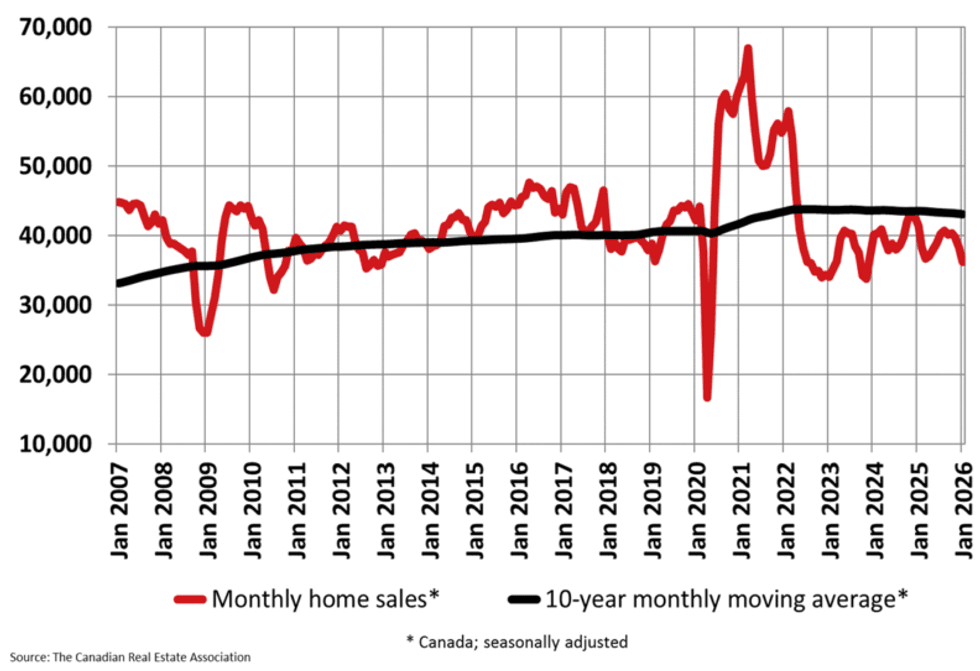 CREA
CREA
 Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)
Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)

 401-415 King Street West. (JLL)
401-415 King Street West. (JLL)
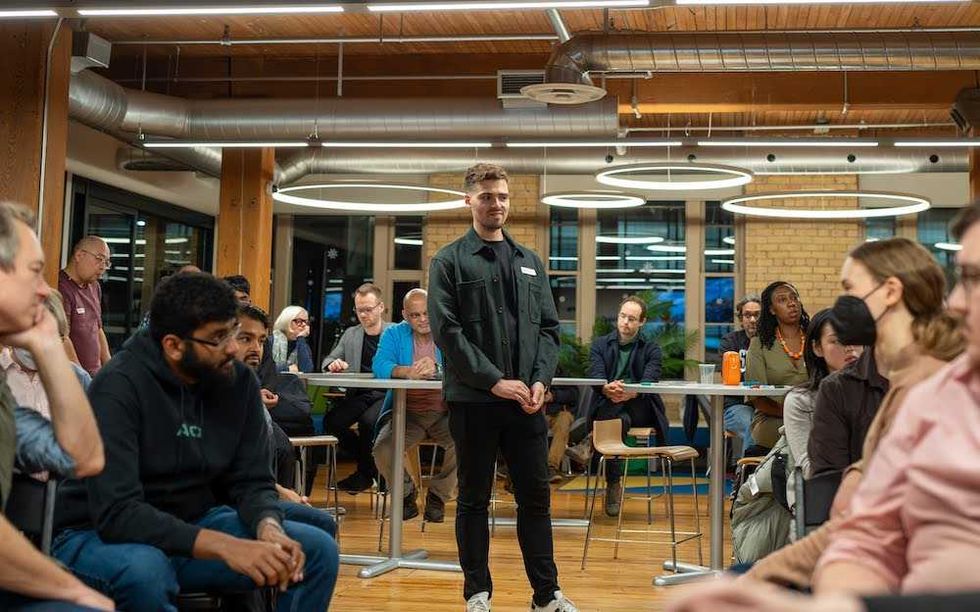 Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.
Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.