Mortgage Stress Test
Understand Canada’s mortgage stress test, how it impacts borrowing power, and what buyers can do to qualify under current regulations.

May 22, 2025
What is a Mortgage Stress Test?
The mortgage stress test is a federal requirement that ensures Canadian borrowers can afford their mortgage payments even if interest rates rise in the future.
Why Mortgage Stress Tests Matter in Real Estate
Introduced by the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI), the mortgage stress test applies to all new mortgage applications, whether insured or uninsured.
To qualify, borrowers must prove they can afford payments at:- The Bank of Canada’s qualifying rate (currently 5.25%); or
- Their contract rate plus 2%
- New home purchases
- Mortgage renewals with a new lender
- Refinancing applications
Its purpose is to reduce the risk of default and ensure borrowers aren’t over-leveraged in fluctuating economic conditions. While it lowers maximum borrowing amounts, it also promotes financial stability.
Buyers who fail the stress test may need to:- Increase their down payment
- Choose a less expensive home
- Work with alternative lenders
Understanding the stress test helps buyers prepare for approval hurdles and align their expectations with what lenders will offer.
Example of a Mortgage Stress Test
A borrower offered a mortgage at 4.7% must qualify at 6.7% (4.7% + 2%) under the stress test, reducing their maximum purchase budget by $50,000.
Key Takeaways
- Required for most mortgage approvals.
- Uses higher qualifying rate to test affordability.
- Reduces max borrowing capacity.
- Aims to prevent financial overextension.
- Crucial to factor into purchase planning.
Related Terms
- Mortgage Pre-Approval
- Debt Service Ratios
- Interest Rate
- Refinance
- Alternative Lender

 205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview
205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview







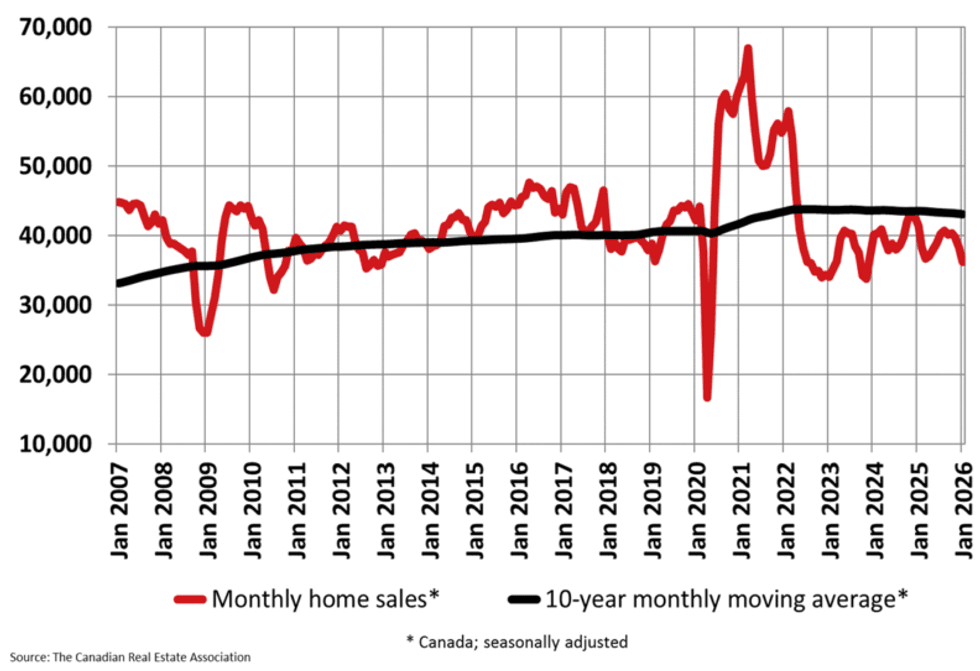 CREA
CREA
 Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)
Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)

 401-415 King Street West. (JLL)
401-415 King Street West. (JLL)
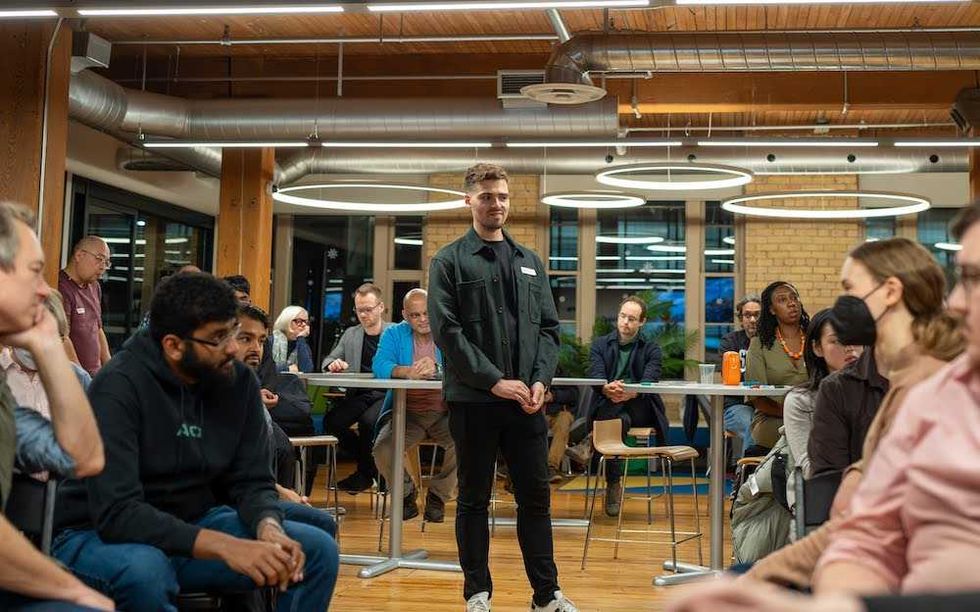 Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.
Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.