Legal Liability
Understand legal liability in Canadian real estate, including common risks for homeowners and landlords, and how to protect against legal claims.

May 22, 2025
What is a Legal Liability?
Legal liability in real estate refers to the legal responsibility a party has for damages or losses arising from actions, omissions, or ownership of property.
Why Legal Liability Matters in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate, homeowners, landlords, and developers can all be held legally liable for a wide range of issues. Common examples include:- Injuries caused by unsafe conditions on a property
- Failure to disclose material defects during a sale
- Breach of contract or lease terms
- Negligent property maintenance or construction
Liability can arise from civil lawsuits, tenant claims, municipal fines, or regulatory infractions. Legal liability extends to personal injury, financial losses, and environmental damage.
To protect themselves, property owners and investors often carry liability insurance, such as general homeowner’s insurance or commercial liability coverage. Understanding one’s legal responsibilities—and ensuring proper documentation and compliance—can help avoid costly disputes or litigation.
Clear contracts, regular inspections, and legal consultation are essential tools for managing legal liability in real estate transactions and ownership.
Example of Legal Liability
A landlord is held legally liable after a tenant slips on an icy walkway that wasn’t salted, resulting in a lawsuit and damages for medical costs.
Key Takeaways
- Refers to responsibility for harm or loss.
- Arises from negligence, omissions, or contract breaches.
- Includes injury claims, financial losses, or fines.
- Insurance can help mitigate risk.
- Must be actively managed through best practices.
Related Terms
- Material Defect
- Disclosure Statement
- Insurance Coverage
- Landlord Responsibilities
- Negligence
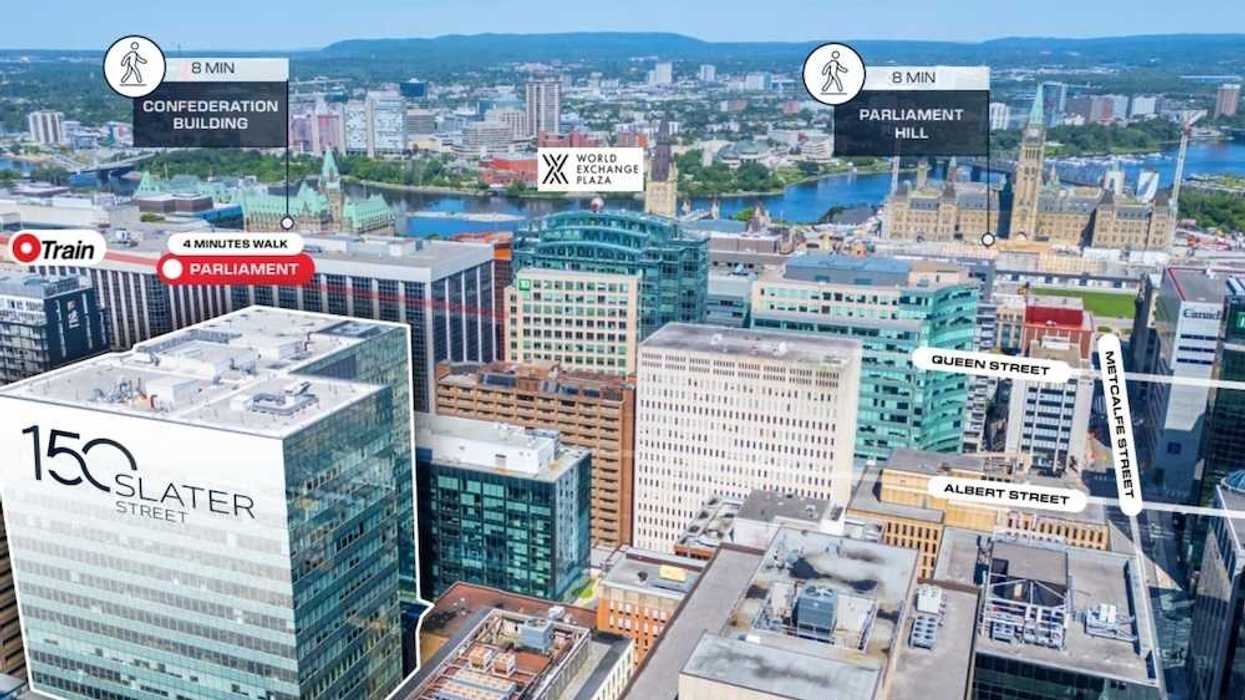
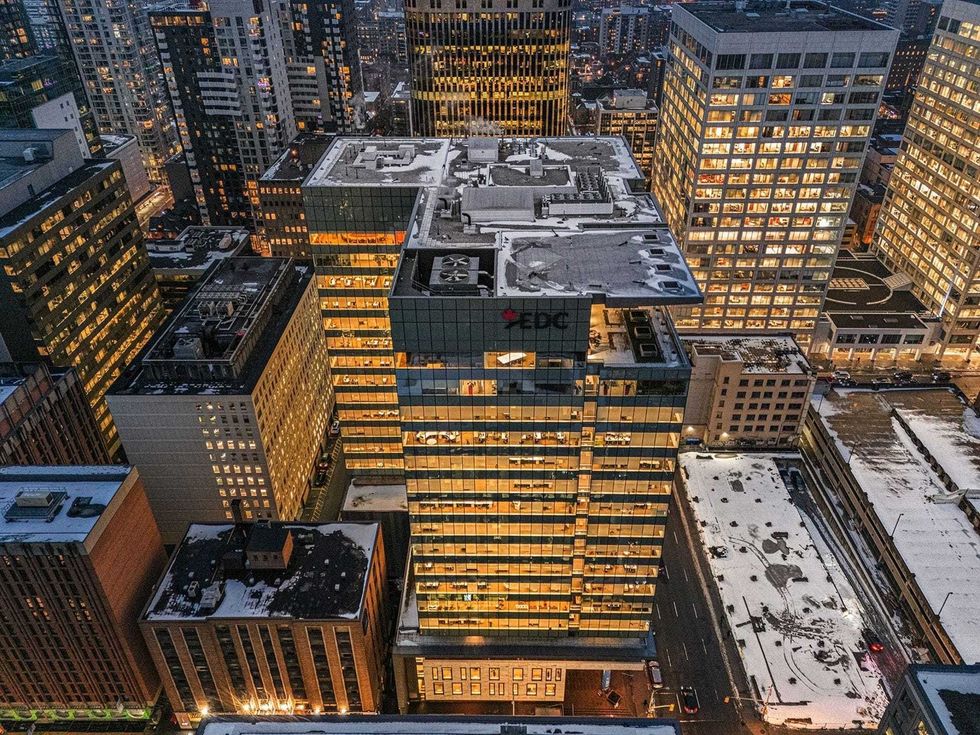
 150 Slater Street in Ottawa. (Regional Group)
150 Slater Street in Ottawa. (Regional Group)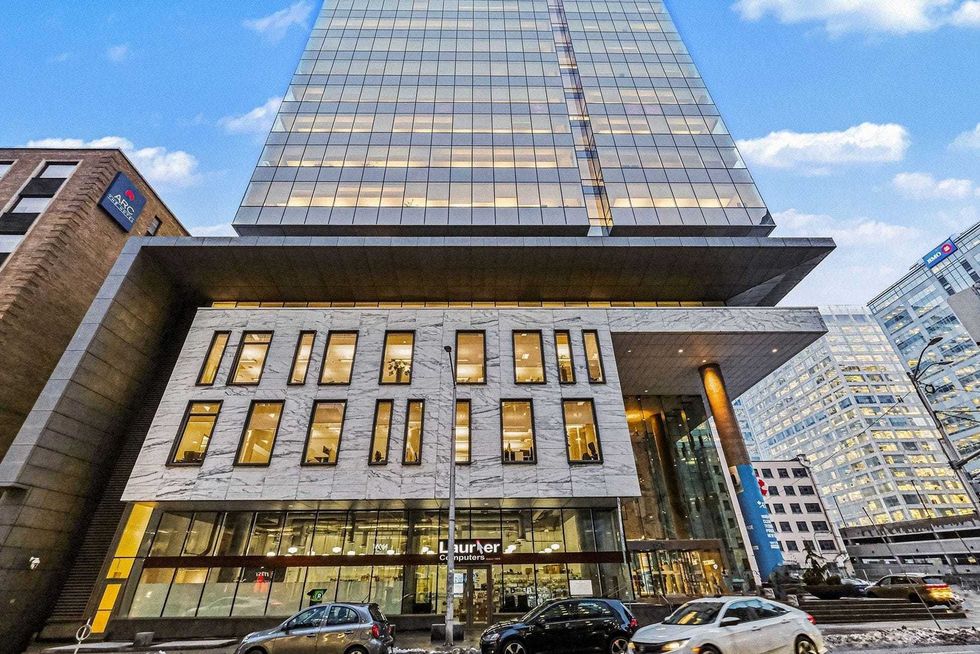 150 Slater Street in Ottawa. (Regional Group)
150 Slater Street in Ottawa. (Regional Group)
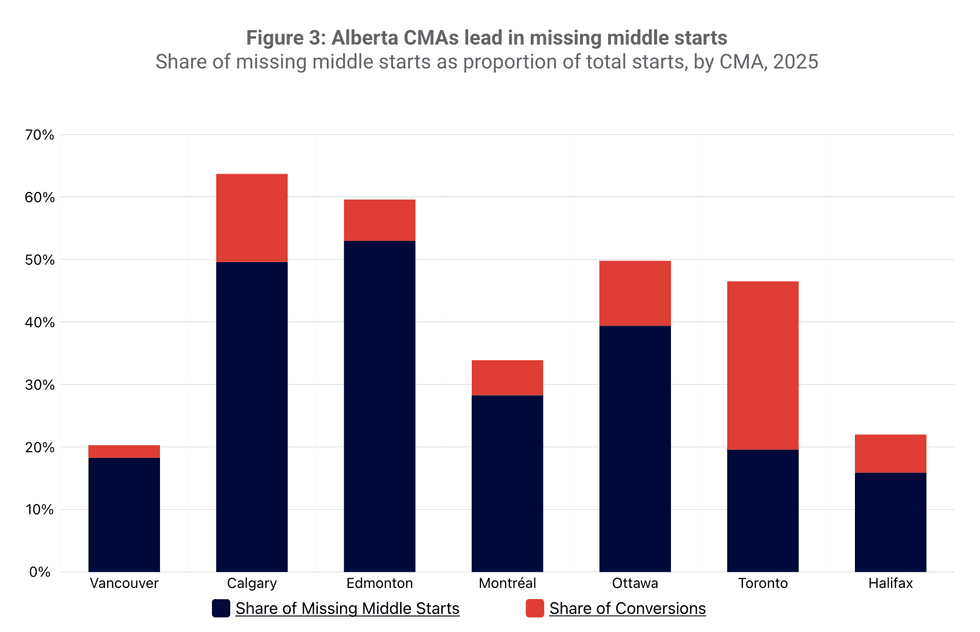 Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC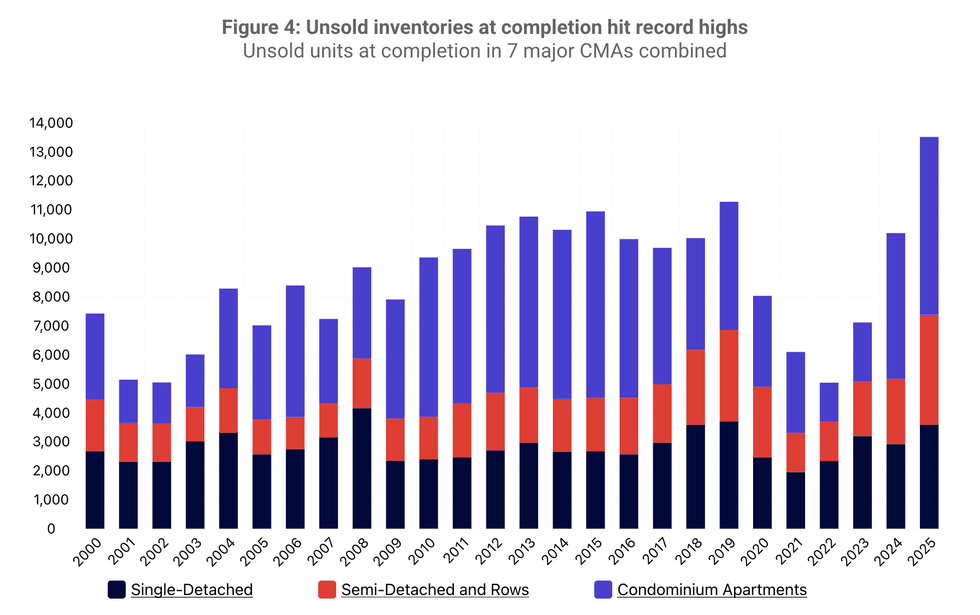 Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
Spring 2026 Housing Supply Report/CMHC
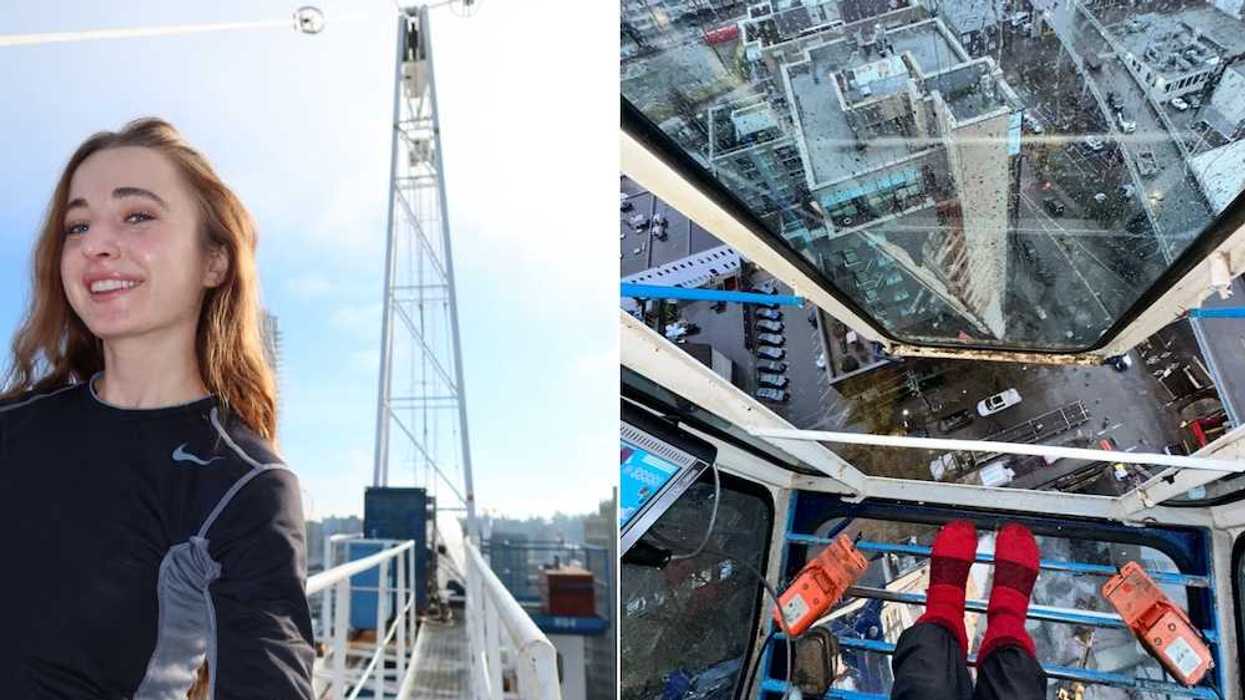
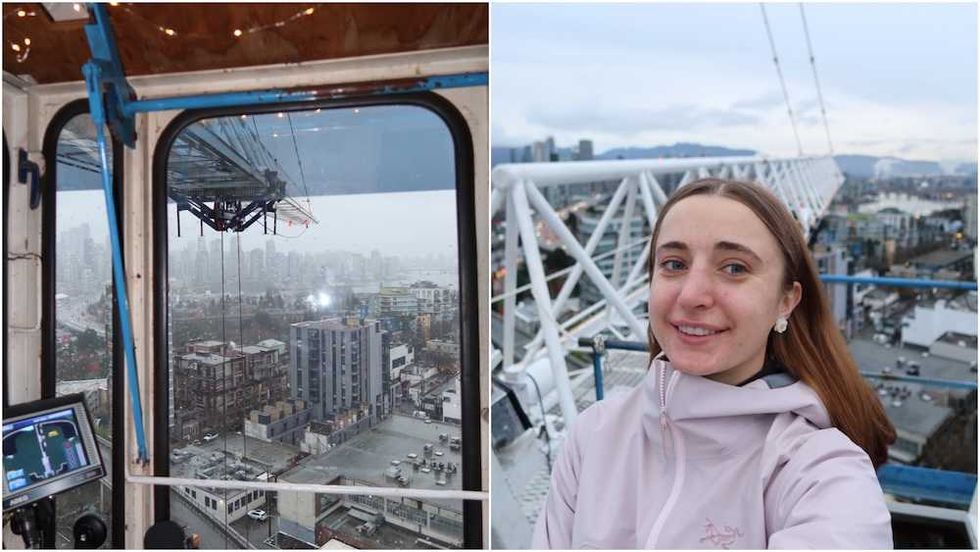





 Manuela Preis/Instagram
Manuela Preis/Instagram
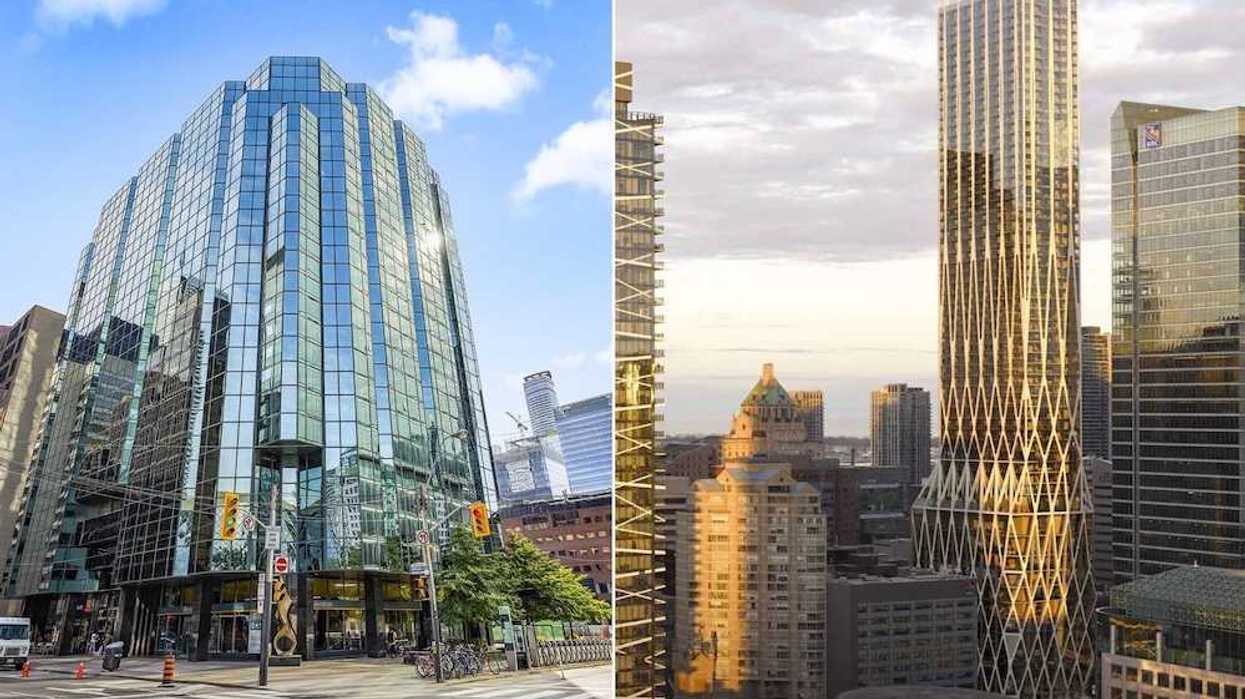
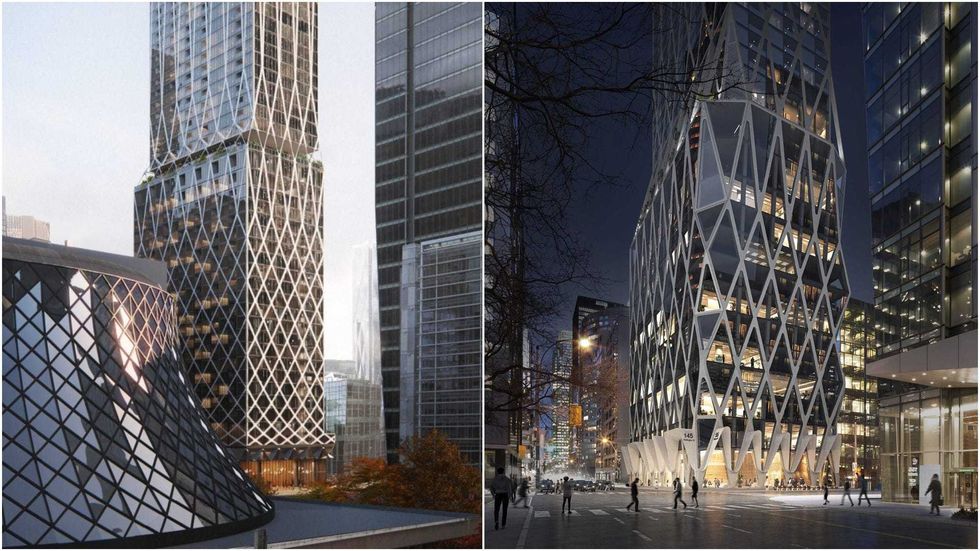



 Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)
Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)