Disposition
Understand disposition in Canadian real estate - what it means, when it happens, and how it affects ownership, taxes, and estate planning.

June 06, 2025
What is a Disposition?
Disposition in real estate refers to the sale, transfer, or disposal of a property or asset by the owner, whether voluntarily or through legal or financial obligation.
Why Dispositions Matter in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate, disposition is a key event that can trigger capital gains tax and mark the end of property ownership.
Disposition includes:
- Selling a property
- Gifting or transferring to a family member
- Foreclosure or expropriation
- Change in use from personal to rental or vice versa
The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) requires that any disposition of property be reported, with capital gains calculated using the adjusted cost base.
Understanding disposition is essential for estate planning, tax reporting, and assessing legal or financial impacts of property sales.
Example of a Disposition in Action
When a homeowner sells a vacation property, it is considered a disposition, and they must report the capital gain to the CRA.
Key Takeaways
- Occurs when property is sold or transferred
- Can be voluntary or court-mandated
- Triggers capital gains tax for non-principal residences
- Must be reported to the CRA
- Relevant for sales, gifts, and estate plans
Related Terms
- Adjusted Cost Base
- Capital Gains Tax
- Legal Title
- Transfer of Ownership
- Estate Planning
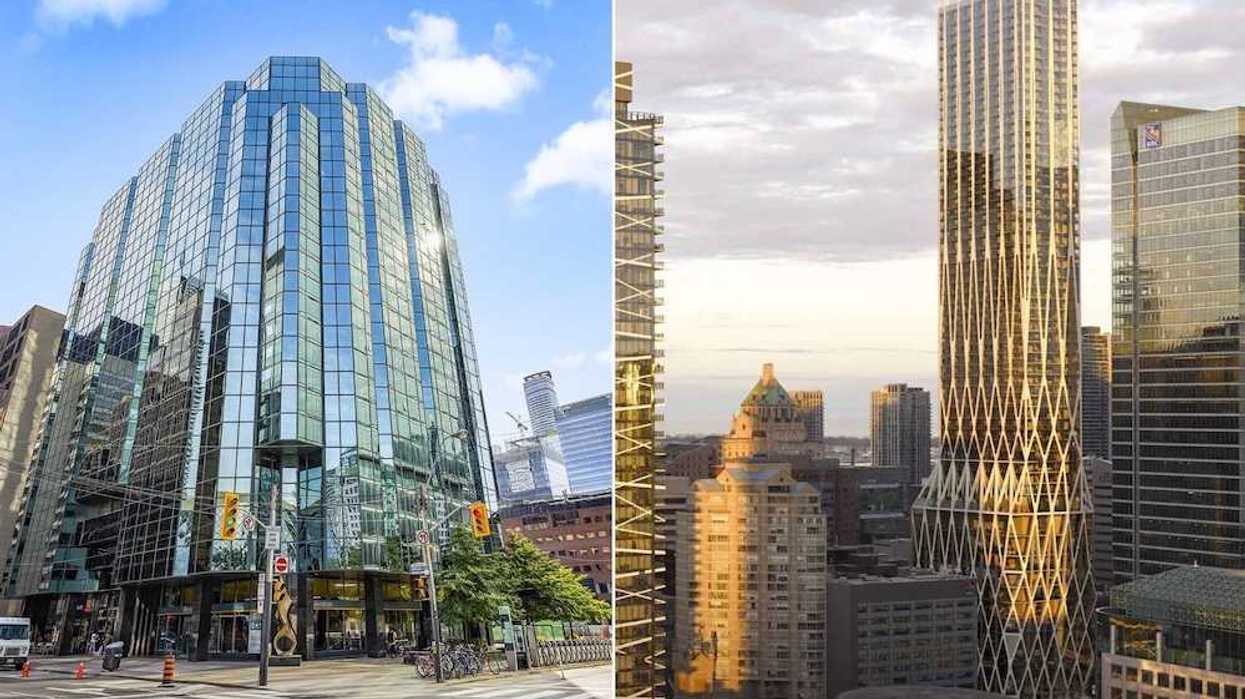
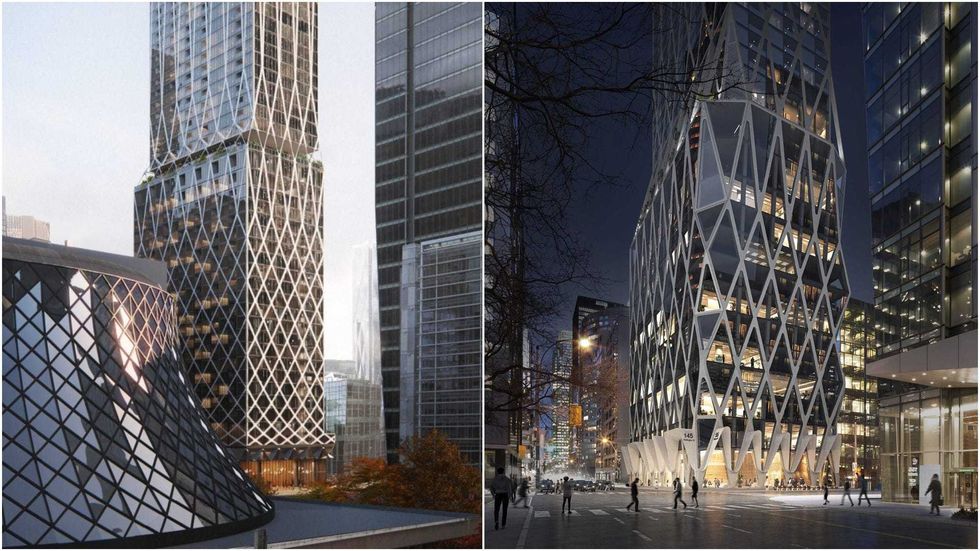

 Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)
Renderings of the 65-storey tower previously proposed for 145 Wellington Street West. (Partisans with Turner Fleischer / SKYGRiD)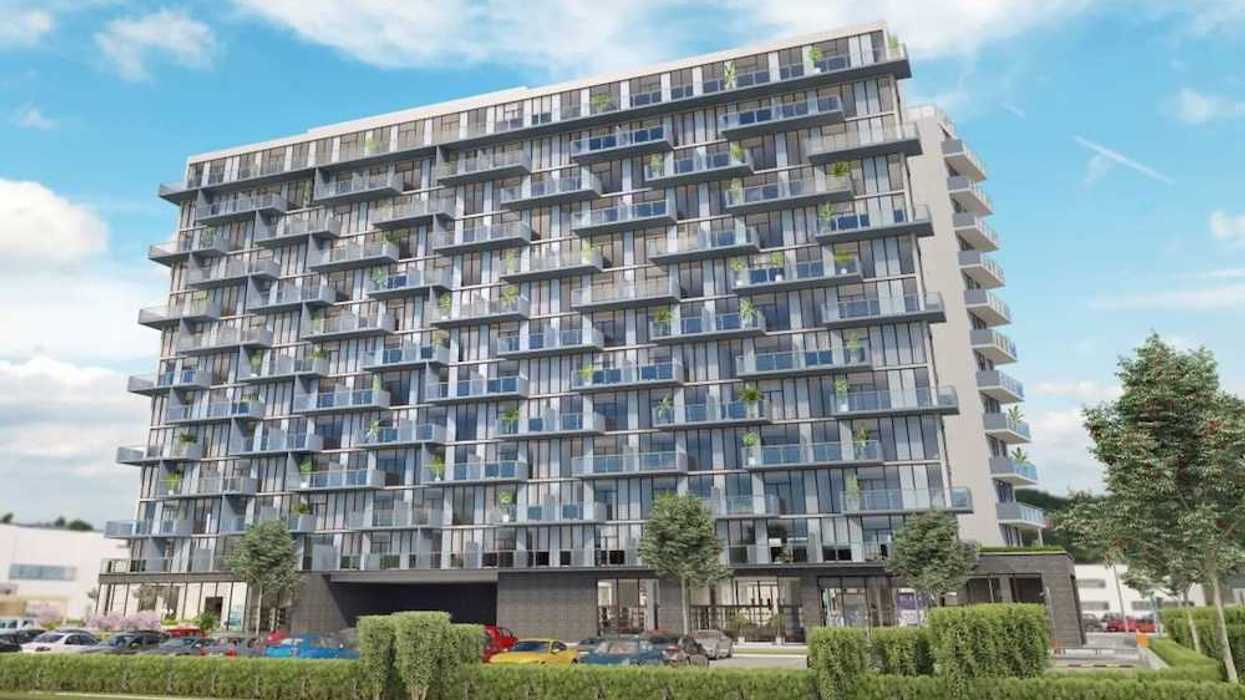





 205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview
205 Queen Street, Brampton/Hazelview
 Christine Boyle and Gregor Robertson. (Government of British Columbia)
Christine Boyle and Gregor Robertson. (Government of British Columbia)

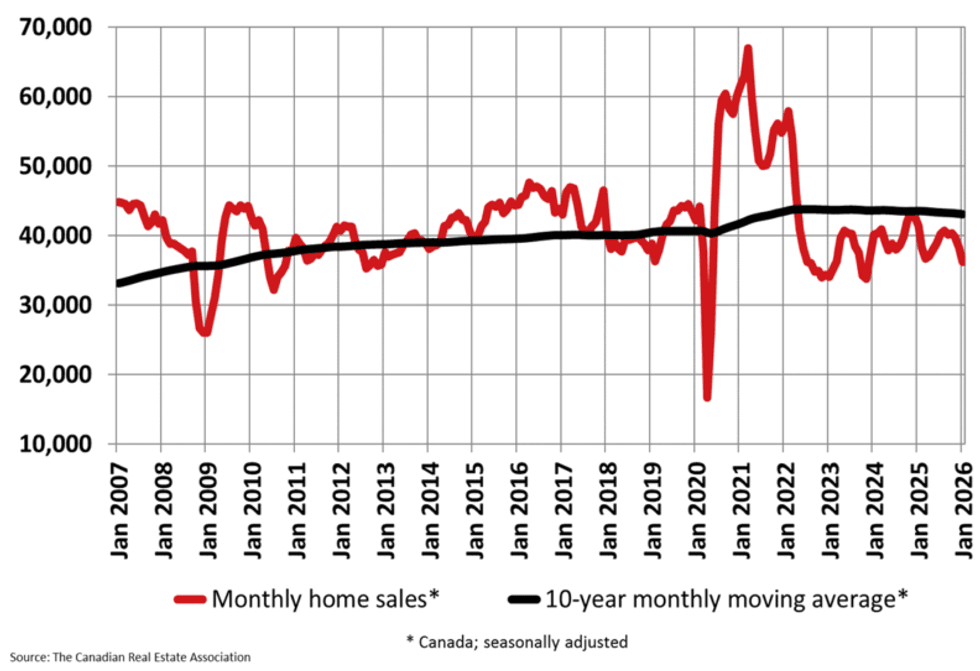 CREA
CREA
 Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)
Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)