Coverage Limit
Explore what a coverage limit is in Canadian real estate insurance, how it protects homeowners, and why selecting the right limit is crucial.

May 22, 2025
What is a Coverage Limit?
A credit score is a numerical rating that reflects a borrower’s creditworthiness and financial reliability based on past credit behavior.
Why a Coverage Limit Matters in Real Estate
In Canadian real estate, coverage limits define the financial ceiling for protection in home insurance policies. They apply to both property protection and liability coverage.
Examples of coverage types include:
- Dwelling limit (e.g., $500,000 for rebuilding a home)
- Personal belongings (e.g., $75,000)
- Liability coverage (e.g., $1 million to $2 million)
Choosing insufficient coverage can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses after a loss. Replacement cost coverage (vs. actual cash value) also impacts the payout.
Understanding coverage limits helps homeowners make informed insurance decisions and secure the level of protection needed for peace of mind.
Example of a Coverage Limit in Action
A homeowner has a $1 million liability coverage limit, which fully protects them in the event of a major injury claim filed by a guest.
Key Takeaways
- Sets the maximum payout on insurance claims.
- Applies to both property and liability.
- Should reflect property value and risk.
- Essential for disaster and lawsuit protection.
- Key insurance planning element.
Related Terms
- Home Insurance
- Property Protection
- Liability Coverage
- Risk Management
- Replacement Cost


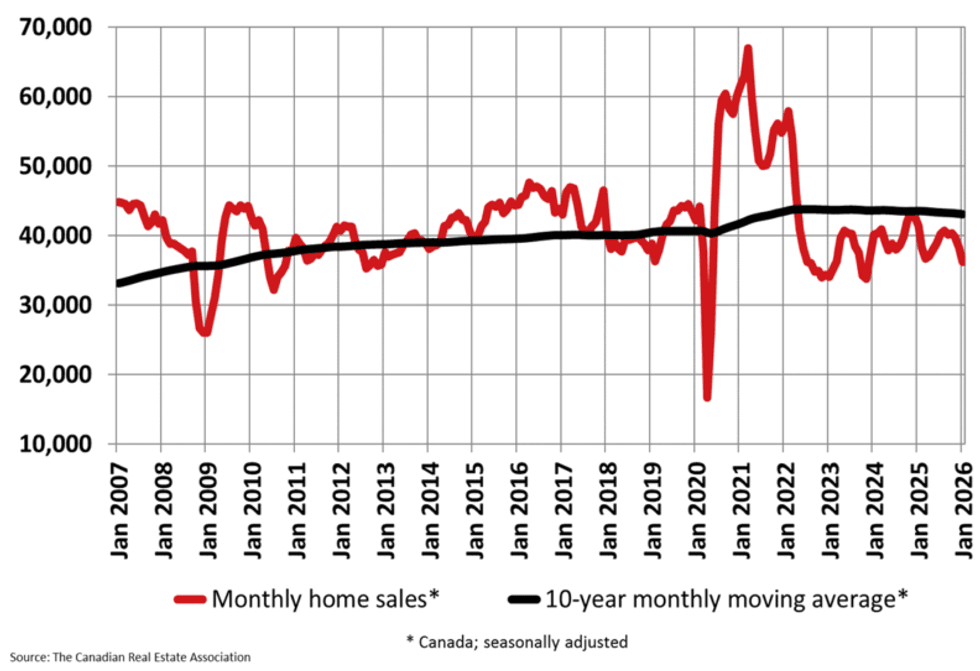 CREA
CREA
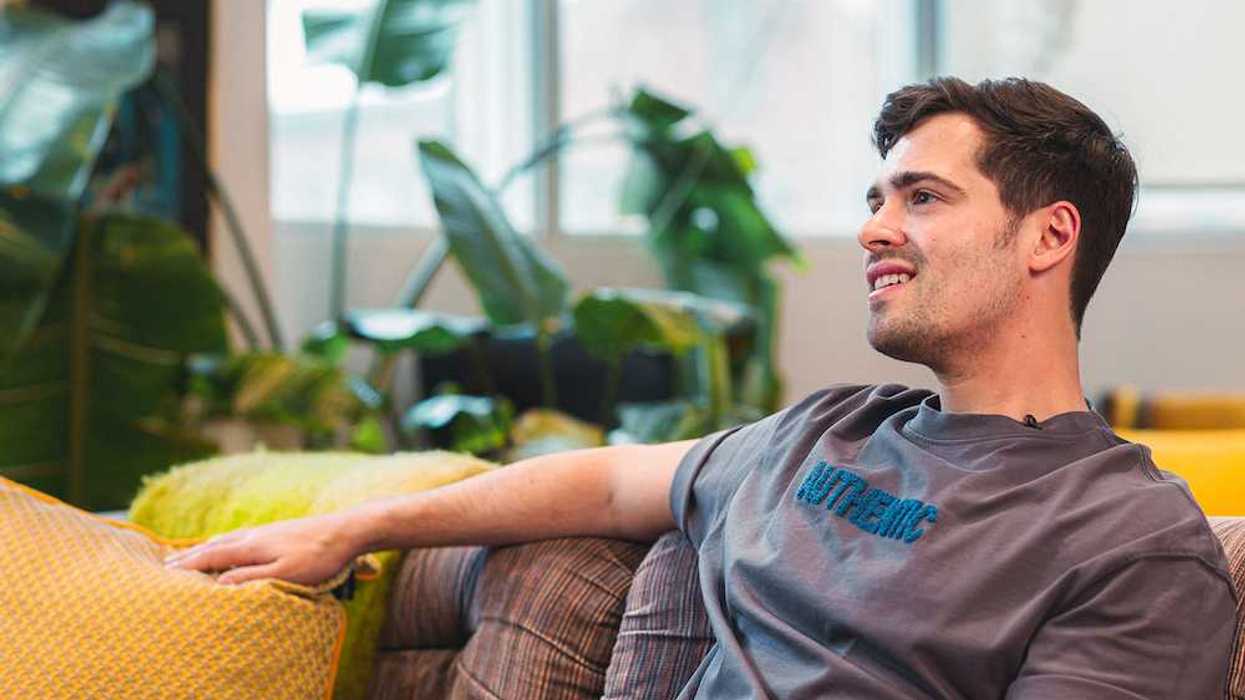





 Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)
Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)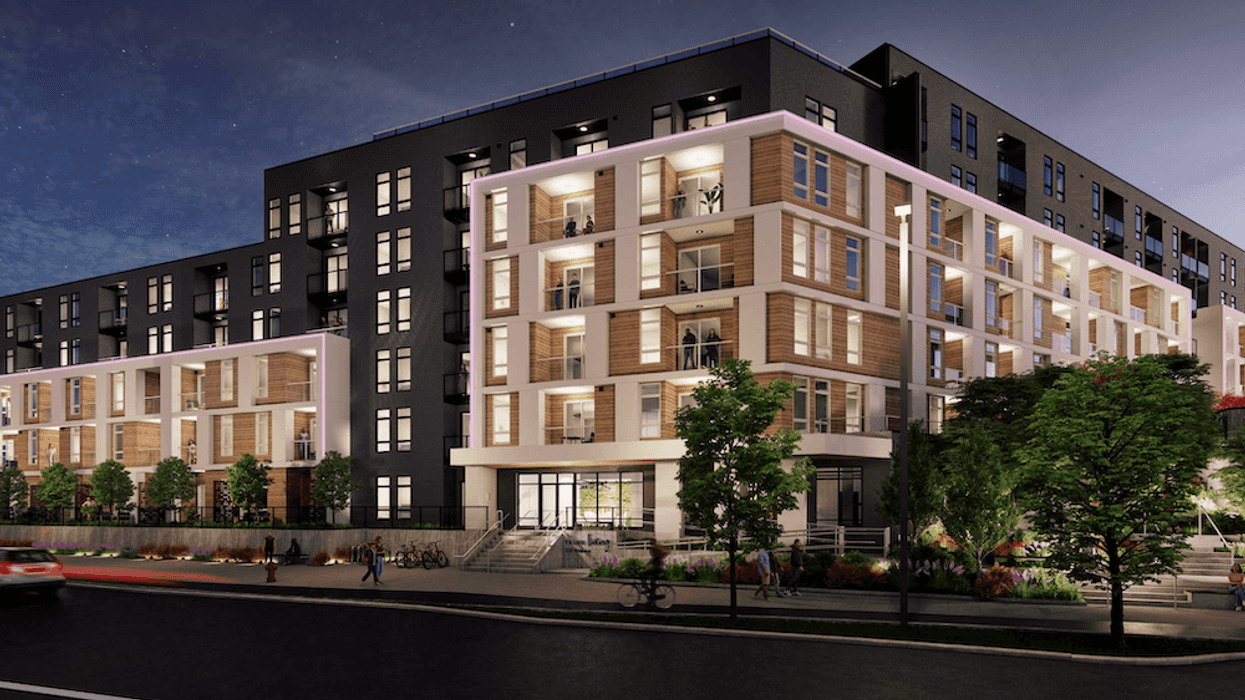
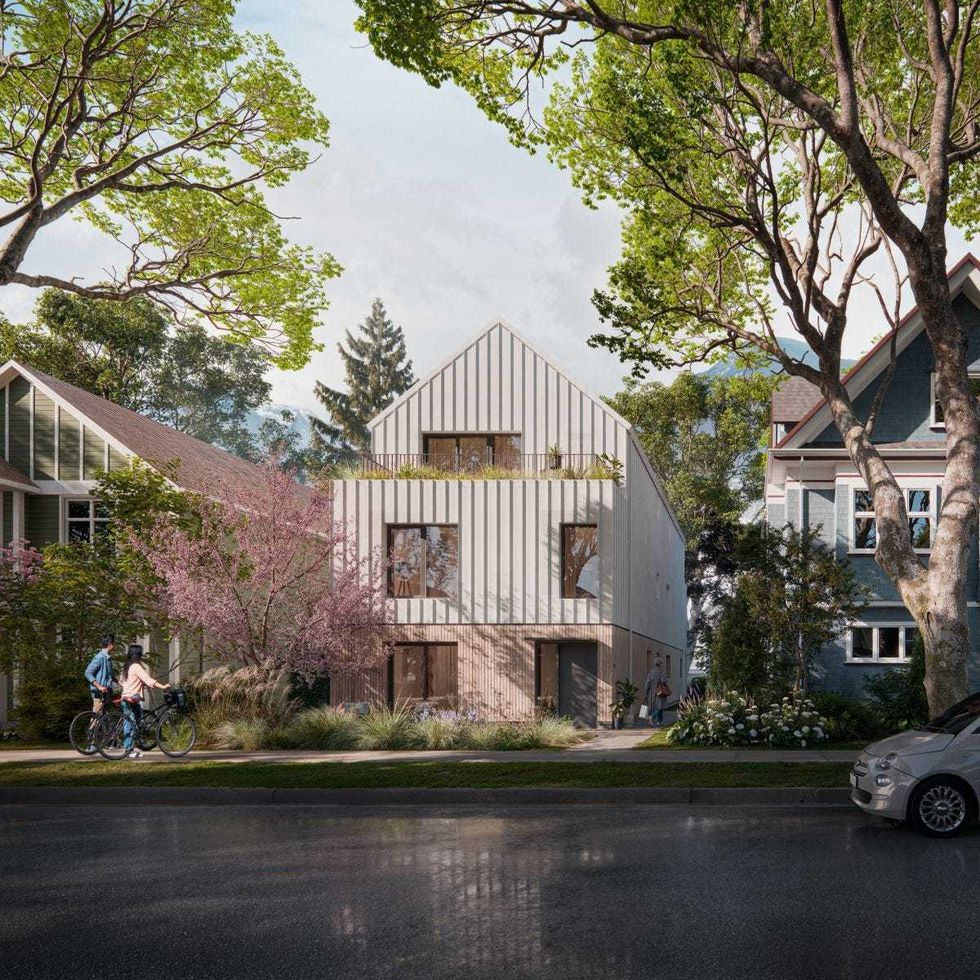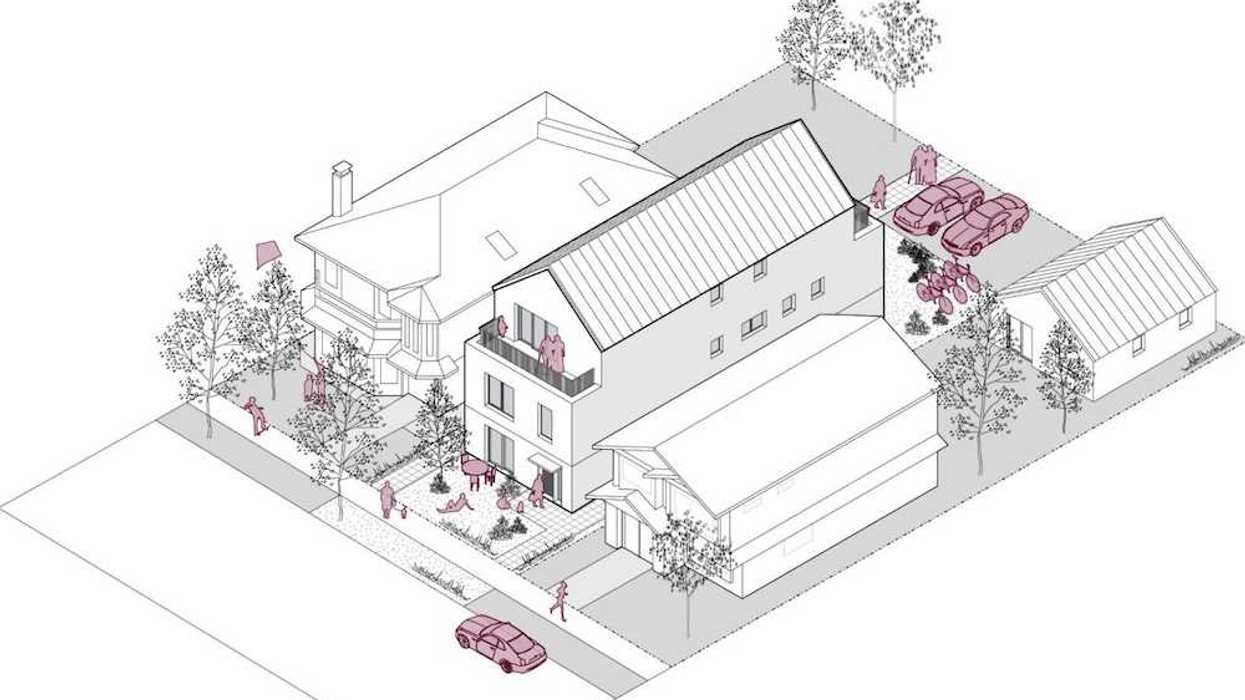
 A rendering of the “BC Fourplex 01” concept from the Housing Design Catalogue. (CMHC)
A rendering of the “BC Fourplex 01” concept from the Housing Design Catalogue. (CMHC)
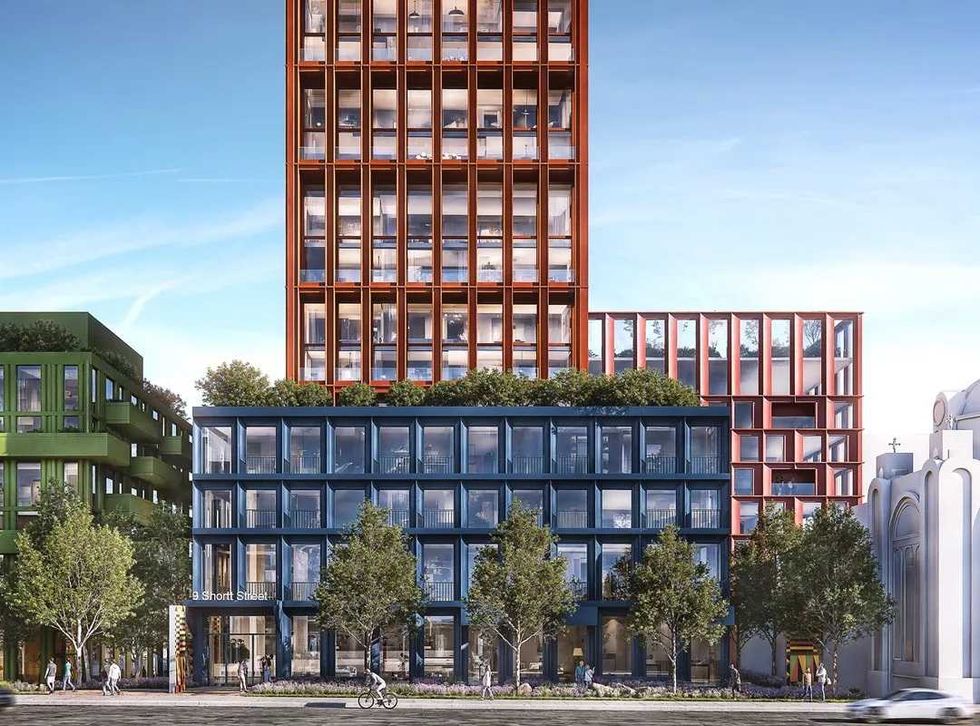 Rendering of 9 Shortt Street/CreateTO, Montgomery Sisam
Rendering of 9 Shortt Street/CreateTO, Montgomery Sisam Rendering of 1631 Queen Street/CreateTO, SVN Architects & Planners, Two Row Architect
Rendering of 1631 Queen Street/CreateTO, SVN Architects & Planners, Two Row Architect Rendering of 405 Sherbourne Street/Toronto Community Housing, Alison Brooks Architects, architectsAlliance
Rendering of 405 Sherbourne Street/Toronto Community Housing, Alison Brooks Architects, architectsAlliance
