Hardship Clause
A hardship clause allows lease modifications or relief when unforeseen circumstances create significant performance challenges.

September 30, 2025
What is a Hardship Clause?
A hardship clause is a contractual provision that allows a party to seek relief from certain obligations when unexpected events make performance extremely difficult or unfair. It differs from force majeure in that it addresses ongoing hardship rather than impossibility. Relief may include rent reductions, deadline extensions, or renegotiation of terms.
Why Hardship Clauses Matter in Real Estate
Hardship clauses matter in real estate because they help allocate risks associated with economic downturns, regulatory changes, or unforeseen market disruptions. They provide flexibility and can preserve relationships by avoiding defaults or litigation. Properly drafted clauses specify qualifying events, notice requirements, and limits to prevent abuse.
Example of a Hardship Clause in Action
A retail tenant invokes a hardship clause after a sudden utility outage severely impacts operations. The landlord and tenant agree to a temporary rent reduction with a review period.
Key Takeaways
- Hardship clauses provide relief in extraordinary circumstances.
- They differ from force majeure provisions.
- Protect tenants and landlords from unexpected burdens.
- Require careful drafting to avoid disputes.
- Preserve lease relationships during difficult times.
Related Terms
- Force Majeure
- Rent Abatement
- Negotiation Protocol
- Material Adverse Change
- Documentation Standards
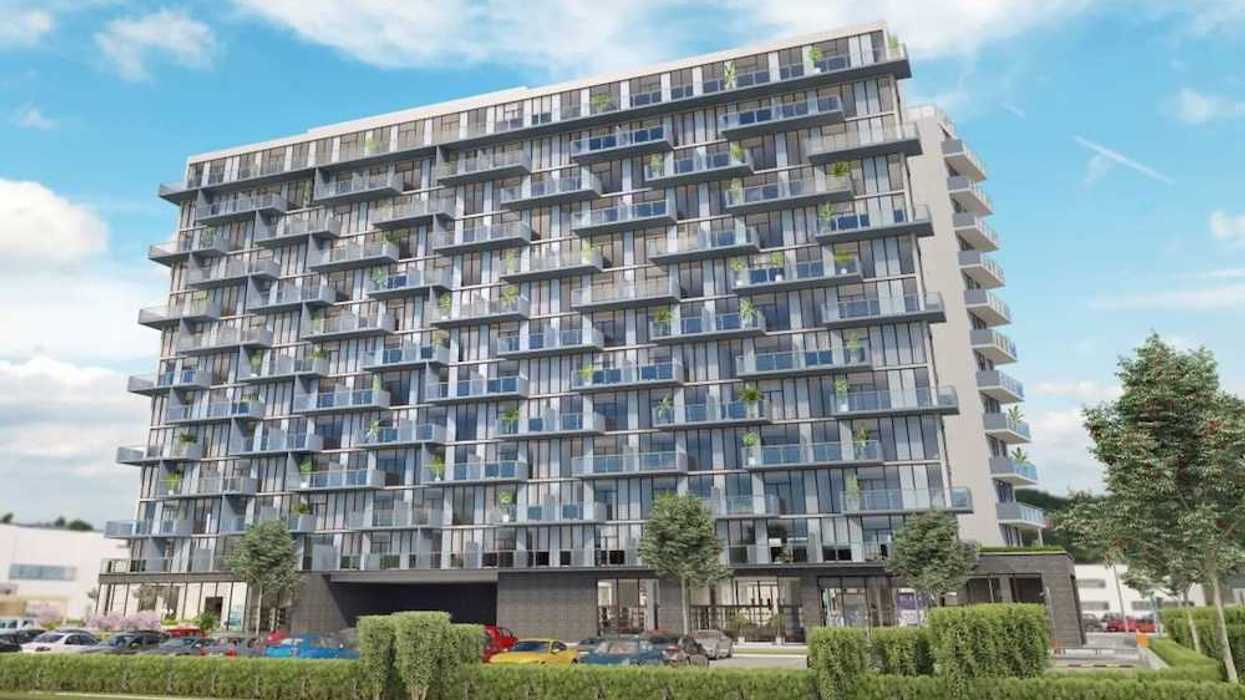
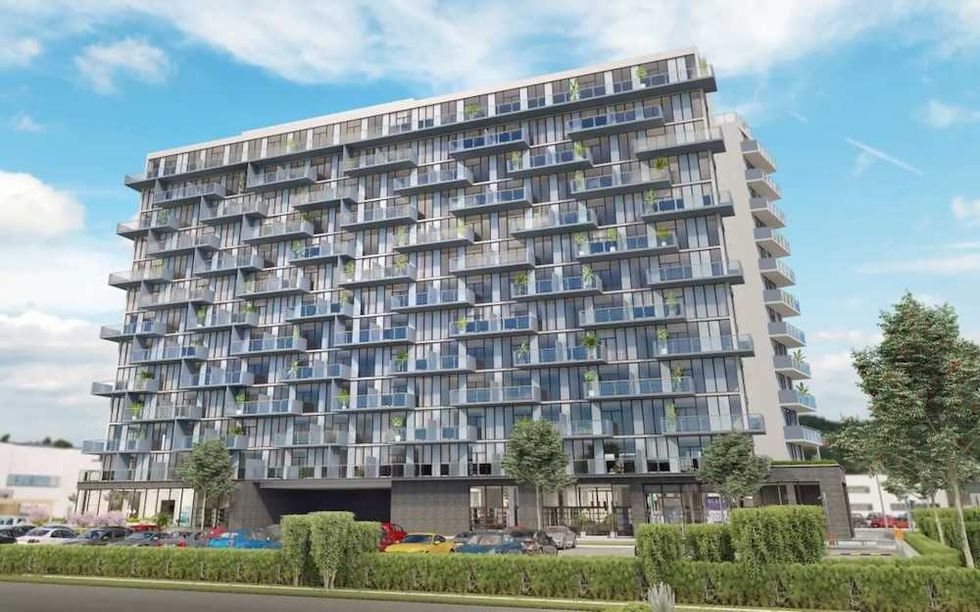
 The LJM Tower at 2782 Barton Street East in Hamilton in June 2025. (Google Maps)
The LJM Tower at 2782 Barton Street East in Hamilton in June 2025. (Google Maps) Ontario Premier Doug Ford and LJM Developments President Liaquat Mian. (LJM Developments)
Ontario Premier Doug Ford and LJM Developments President Liaquat Mian. (LJM Developments)











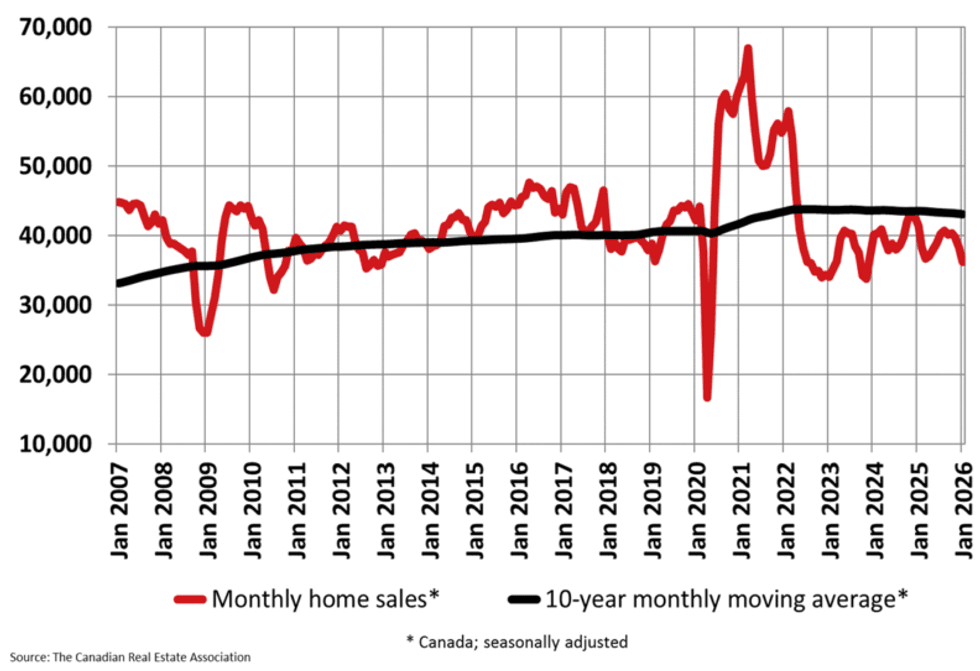 CREA
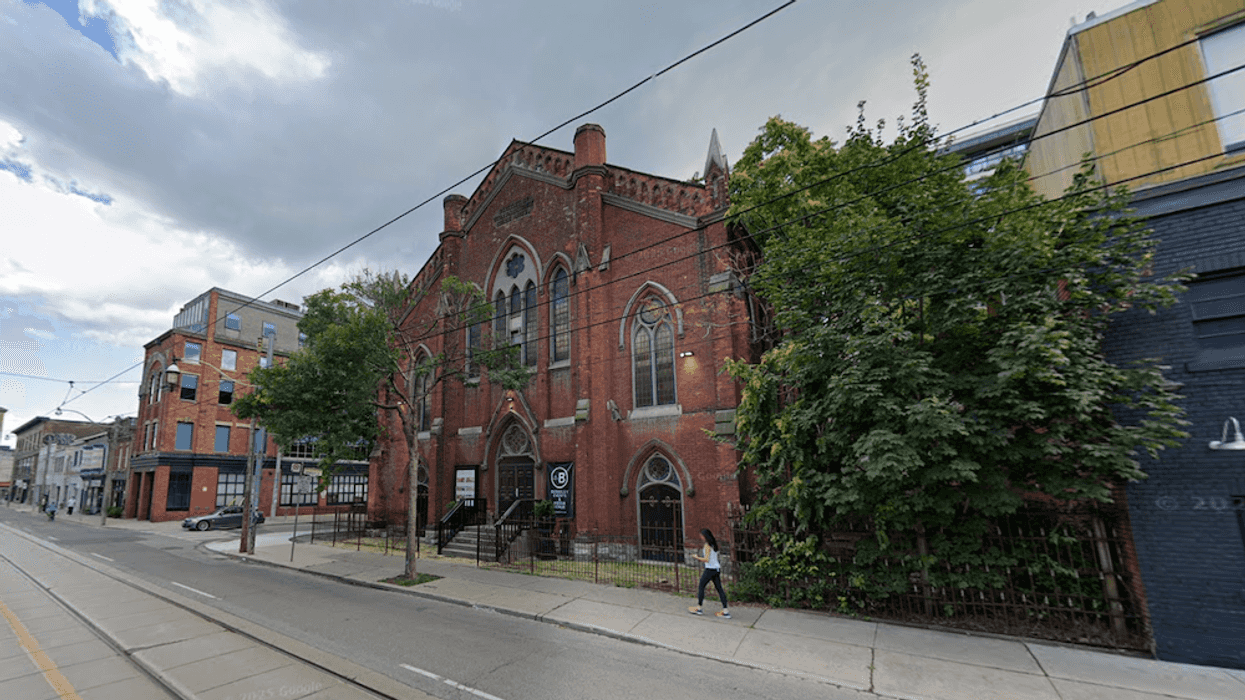
CREA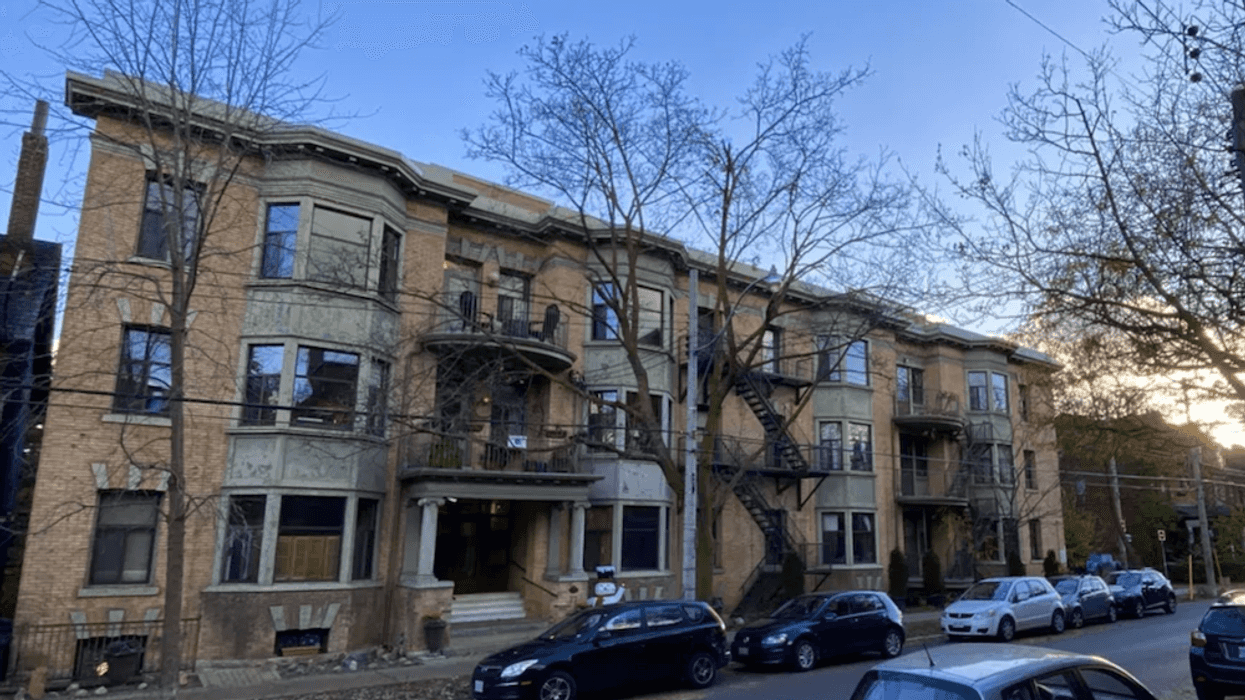
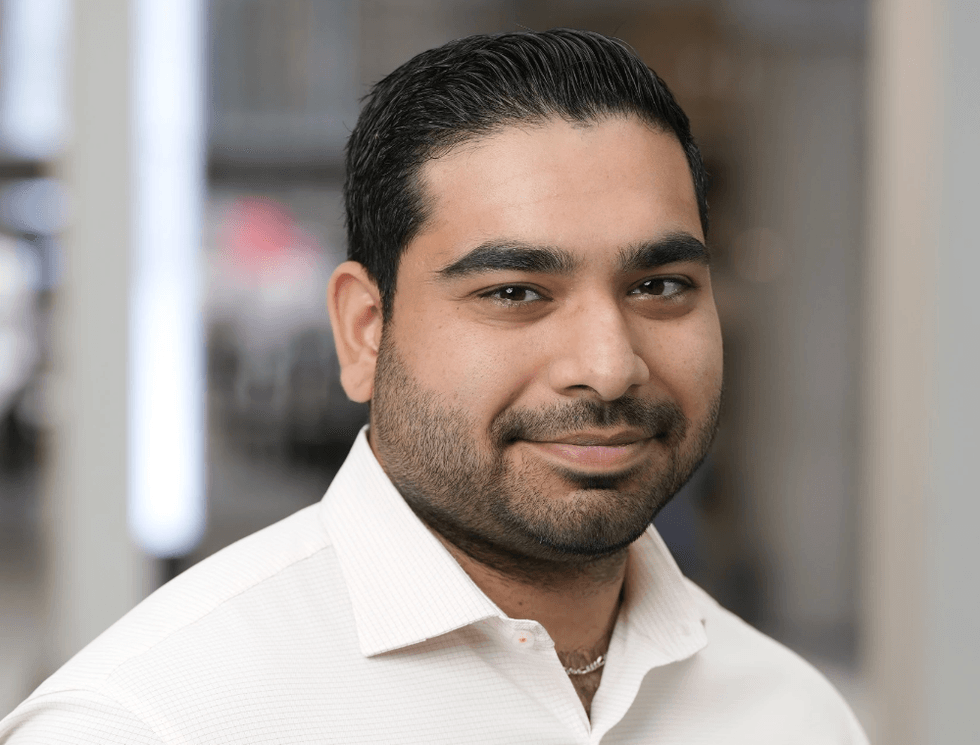 Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)
Liam Gill is a lawyer and tech entrepreneur who consults with Torontonians looking to convert under-densified properties. (More Neighbours Toronto)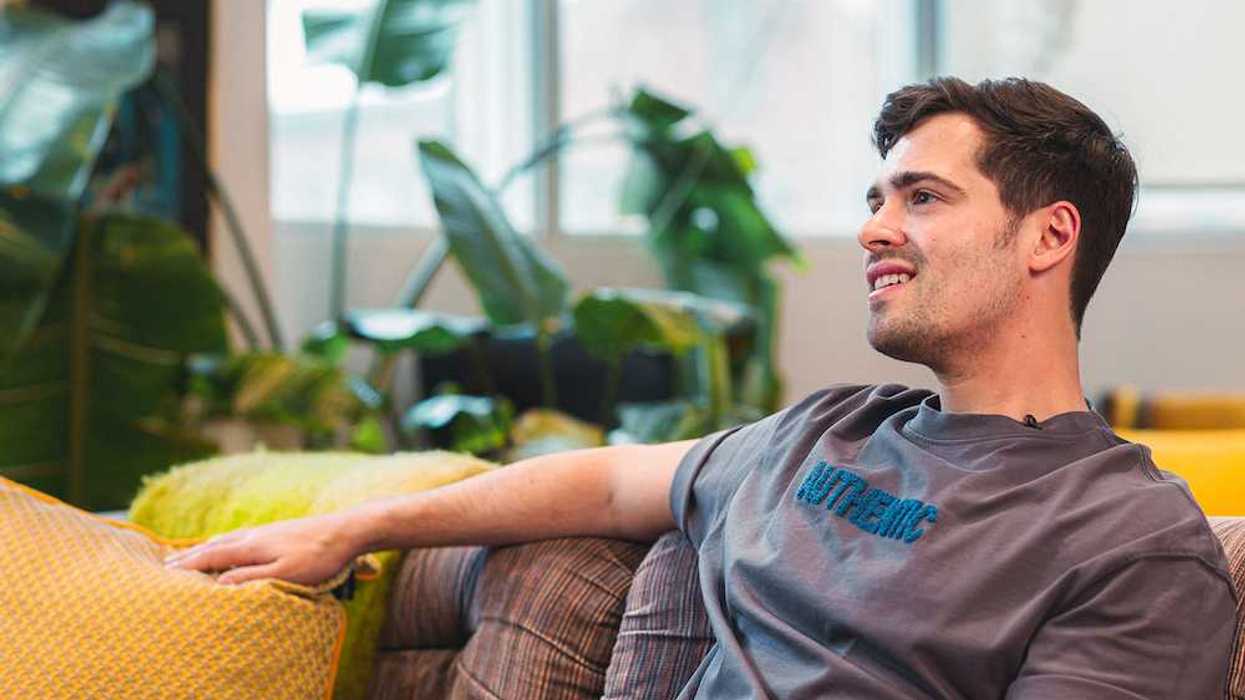
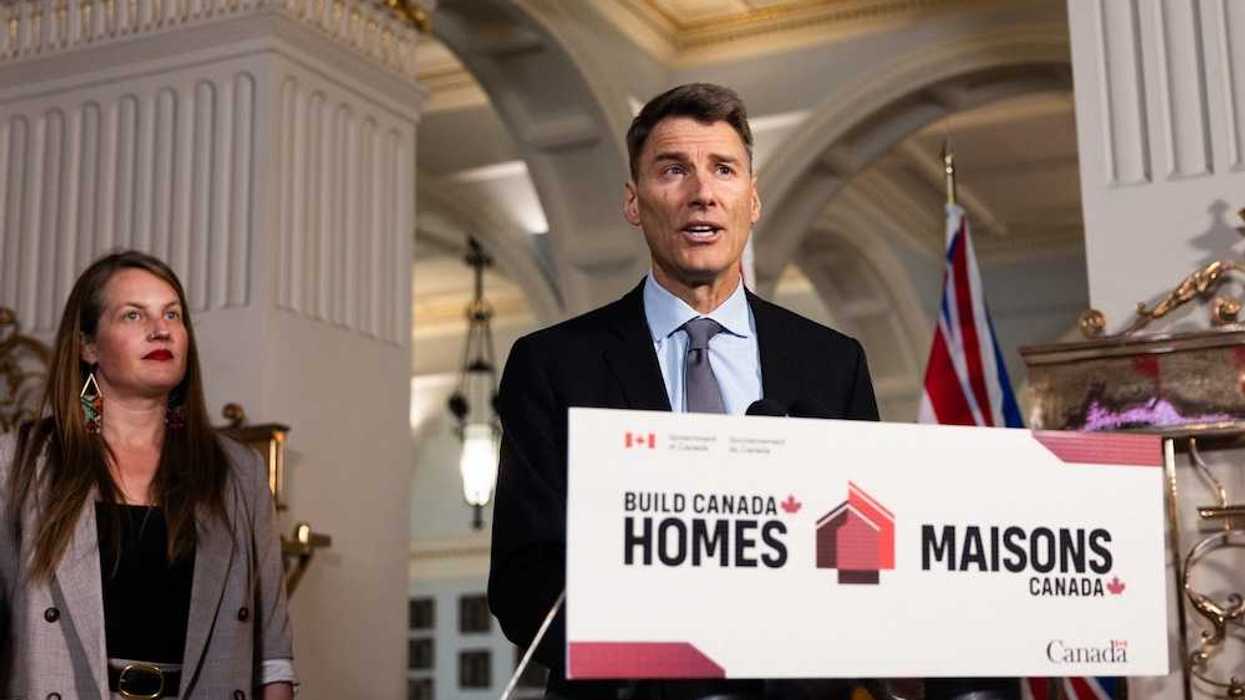
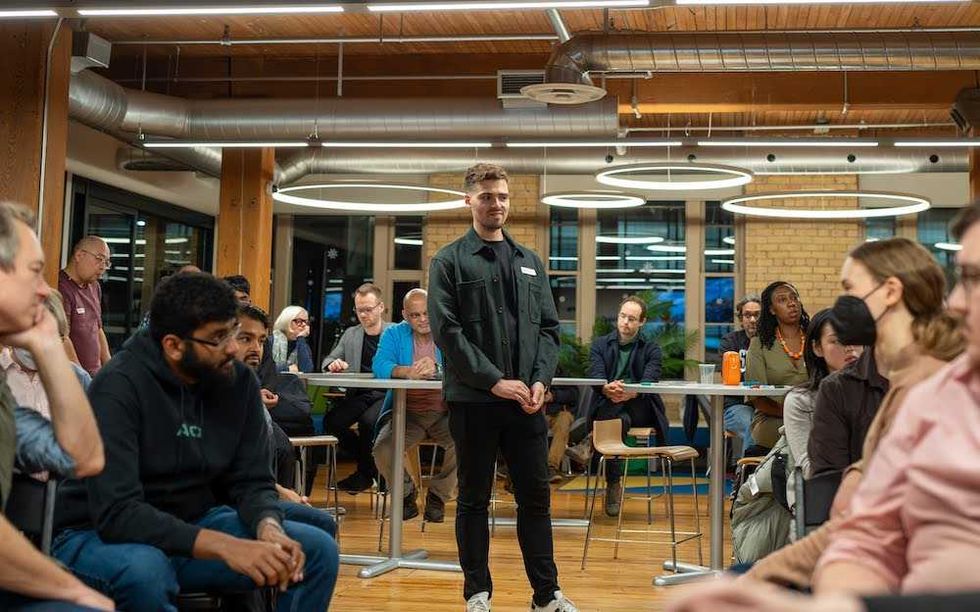 Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.
Eric Lombardi at an event for Build Toronto, which is the first municipal project of Build Canada. Lombardi became chair of Build Toronto in September 2025.
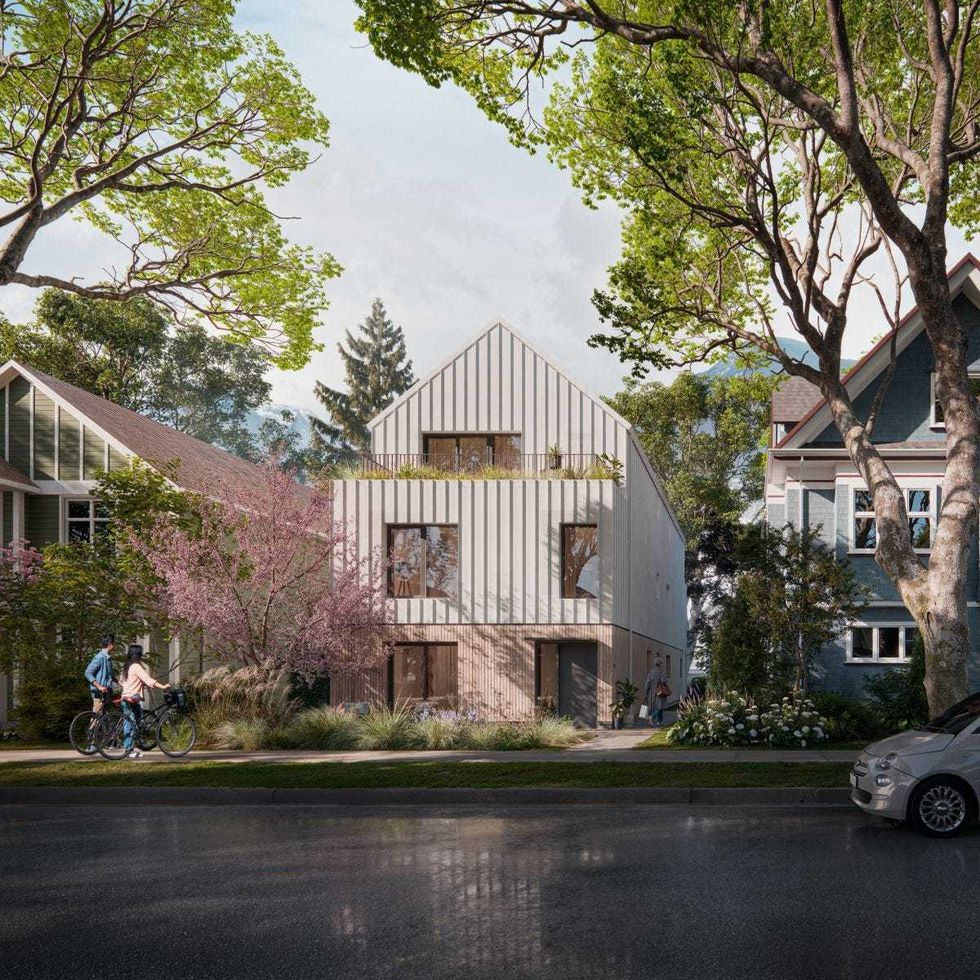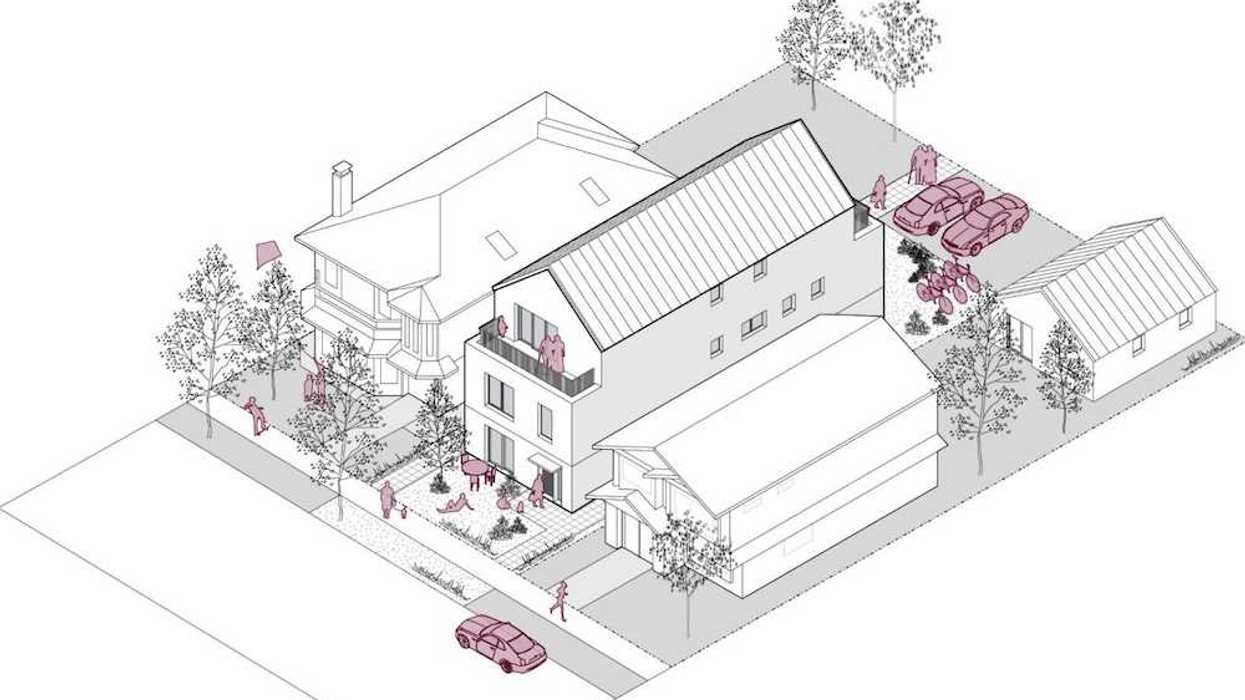
 A rendering of the “BC Fourplex 01” concept from the Housing Design Catalogue. (CMHC)
A rendering of the “BC Fourplex 01” concept from the Housing Design Catalogue. (CMHC)